
The modern business arena is defined by a relentless pursuit of customer loyalty and operational efficiency. In an age where customer expectations are higher than ever, and data flows like a torrent, merely reacting is no longer sufficient. Proactive engagement, personalized interactions, and streamlined processes are the hallmarks of market leaders. This is precisely where the symbiotic power of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Marketing Automation emerges as indispensable.
💡 Key Takeaways
- Seamless integration of CRM and marketing automation boosts efficiency and ROI.
- Personalized customer journeys are enabled by unified data.
- Automating tasks frees up teams for strategic initiatives.
- Improved data insights lead to more effective campaigns and sales conversions.
“The true power of CRM and marketing automation isn’t just efficiency, but the ability to create deeply personalized, scalable customer experiences that were once impossible.”
— Dr. Lena Kapoor, Chief Marketing Technologist
These are not just buzzwords; they are the strategic pillars upon which sustainable growth, profound customer relationships, and scalable marketing efforts are built. A well-implemented CRM system provides the holistic view of your customer, transforming interactions from transactional to relational. Complementing this, marketing automation ensures that these relationships are nurtured consistently and efficiently, delivering the right message to the right person at the right time, every time.
As the Editor-in-Chief of this esteemed publication, I am proud to present “CRM & Marketing Automation: The Ultimate Guide.” This meticulously crafted resource distills years of industry expertise and cutting-edge insights into a single, comprehensive compendium. From fundamental concepts and platform selection to advanced integration strategies and best practices, this guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge and tools to transform your customer engagement and elevate your business to unprecedented heights. Consider this your definitive roadmap to mastering the digital frontier of customer experience.
“The true power of CRM and marketing automation isn’t just efficiency, but the ability to create deeply personalized, scalable customer experiences that were once impossible.”
— Dr. Lena Kapoor, Chief Marketing Technologist
In This Article
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- → CRM Fundamentals & Selection
- — The Foundational Pillars of CRM
- — Why CRM is Non-Negotiable in Today’s Market
- — Navigating CRM Selection: A Practitioner’s Checklist
- — CRM vs. Marketing Automation: Distinct Roles & Integrated Power
- → Specific CRM Platform Guides
- — Salesforce Sales Cloud
- — HubSpot CRM Suite (Sales Hub, Marketing Hub, Service Hub)
- — Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales
- — Zoho CRM
- → CRM & Marketing Automation Features & Best Practices
- — Centralized Customer Data & Contact Management
- — Lead Management & Sales Pipeline Automation
- — Marketing Campaign Automation & Personalization
- — Analytics, Reporting & ROI Measurement
- — Integrations & Ecosystem Management
- → Marketing Automation Strategies & Implementation
- — Laying the Strategic Foundation: More Than Just Tools
- — Selecting Your Marketing Automation Powerhouse
- — The Implementation Playbook: From Concept to Campaign
- → Integrations & Workflow Optimization
- — The Imperative of Integration: Breaking Down Data Silos
- — Types of Integration Architectures: Choosing Your Path
- — Core Systems Requiring Integration for Workflow Optimization
- — Workflow Optimization in Action: Practical Scenarios
- — Advanced Strategies & Common Pitfalls
- → Specific Marketing Automation Platforms
- — HubSpot Marketing Hub
- — Salesforce Marketing Cloud Account Engagement (Pardot)
- — Adobe Marketo Engage
- — ActiveCampaign
- — Klaviyo
- → Related Business Software & Tools
- — Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
- — Customer Service & Support Platforms
- — Analytics & Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
- — Accounting & Financial Management Software
- — E-commerce Platforms
- — Content Management Systems (CMS) & Website Builders
- — Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
CRM Fundamentals & Selection
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is far more than just software; it’s a strategic approach to managing a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. At its core, CRM aims to improve business relationships to drive growth, customer retention, and service delivery. It provides a centralized hub for all customer-related data and activities, offering a holistic, 360-degree view of the customer.
The Foundational Pillars of CRM
Understanding these pillars is crucial before even thinking about specific platforms. A robust CRM strategy integrates capabilities across three primary business functions: Sales, Marketing, and Customer Service.
- Sales Management: This is often the most visible aspect of CRM. It encompasses lead management, opportunity tracking, pipeline visibility, sales forecasting, contact management, and automation of repetitive sales tasks. A CRM empowers sales teams to work more efficiently, prioritize leads, and close deals faster.
- Marketing Automation: While often a distinct system, tightly integrated marketing automation within a CRM or a standalone platform that syncs with CRM allows for personalized campaigns, lead nurturing, email marketing, social media management, and campaign performance tracking. This ensures marketing efforts are targeted and measurable, feeding qualified leads directly to sales.
- Customer Service & Support: CRM provides tools for managing customer inquiries, service requests, issue tracking, and knowledge bases. It enables support teams to access complete customer histories, leading to faster resolution times and improved customer satisfaction. Features often include ticketing systems, self-service portals, and chat integration.
- Data & Analytics: A critical, underlying pillar. CRM systems collect vast amounts of customer data, which, when analyzed, provides invaluable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, marketing effectiveness, and service trends. This data-driven approach is essential for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement.
Why CRM is Non-Negotiable in Today’s Market
Beyond operational efficiency, CRM is fundamental to competitive advantage. It’s about building deeper, more profitable relationships. A unified customer view enables personalization at scale, which is no longer a luxury but an expectation. As highlighted by Forrester Research, companies that prioritize customer experience (CX) and strategically manage customer data (a core output of effective CRM) typically see higher customer retention and revenue growth (Forrester.com).
Navigating CRM Selection: A Practitioner’s Checklist
Choosing the right CRM is a strategic decision that impacts every customer-facing part of your business. Resist the urge to rush into demos. Start with introspection.
1. Define Your Business Needs & Goals (The ‘Why’)
Before looking at features, understand the pain points and desired outcomes.
- Current Challenges: What specific problems are you trying to solve? (e.g., losing track of leads, inconsistent customer data, slow response times, lack of sales forecasting).
- Key Stakeholders & User Roles: Who will use the CRM? Salespeople, marketers, customer service agents, management? Document their specific needs and daily tasks.
- Integrations: What existing systems MUST your CRM connect with? (e.g., ERP, accounting software like QuickBooks or Xero, marketing automation platforms, e-commerce platforms like Shopify, communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams).
- Budget & Resources: Be realistic about initial licensing costs, implementation fees, training, and ongoing maintenance. Consider both capital expenditure and operational expenditure.
- Scalability Needs: How many users today? How many in 1, 3, 5 years? Do you anticipate significant growth or new business lines?
2. Understand CRM System Categories & Examples
The market is vast. CRMs broadly fall into categories based on target company size and feature sets:
- Enterprise-Grade: Designed for large organizations with complex needs, extensive customization requirements, and significant integration demands. Examples include Salesforce Sales Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and sometimes highly customized versions of SAP CRM or Oracle CRM. These are powerful but come with higher costs and complexity.
- Mid-Market/SMB Focused: Offer robust feature sets balanced with ease of use and quicker implementation for small to medium-sized businesses. This is often where the most competitive innovation happens. Examples include HubSpot CRM (known for its freemium model and marketing/sales hub integration), Zoho CRM (a comprehensive suite at competitive pricing), Pipedrive (focused heavily on sales pipeline visualization), and monday.com CRM (flexible, visual workflow management).
- Niche/Industry-Specific: Some CRMs are built for specific industries (e.g., healthcare, real estate, financial services) with tailored features and compliance. Evaluate if a generic CRM can be customized or if a specialized solution is truly necessary.
3. Critical Evaluation Criteria During Selection
Once you have a shortlist, evaluate based on these factors:
- User Experience (UX/UI): Is it intuitive? If users don’t adopt it, it’s a wasted investment. Prioritize ease of use and a clean interface.
- Customization & Flexibility: Can it adapt to your unique workflows, reporting needs, and data fields without excessive coding?
- Reporting & Analytics: Does it provide the insights you need to track KPIs, forecast, and make informed decisions? Look for custom report builders and dashboard capabilities.
- Integration Ecosystem: Beyond your initial requirements, what other tools does it integrate with? A rich app marketplace is a good sign.
- Mobile Accessibility: Is there a robust mobile app for your on-the-go teams?
- Vendor Support & Training: What level of support is offered? Are there comprehensive training resources, academies, or certifications available for your team?
- Security & Compliance: Essential for protecting sensitive customer data. Ensure it meets relevant industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA if applicable).
4. The Selection Process: A Practical Roadmap
- Requirements Gathering & Documentation: Involve future users early. Create a detailed RFI/RFP document outlining your specific needs, technical requirements, and budget.
- Vendor Shortlisting: Based on your documented needs, narrow down to 3-5 vendors that appear to be the best fit. Don’t be swayed by aggressive sales pitches alone.
- Demos & Proof of Concept (POC): Request personalized demos that address your specific use cases. Better yet, ask for a trial or a “proof of concept” period where you can test the system with a small subset of your real data and key users. This is critical for uncovering usability issues.
- Reference Checks: Speak to current customers of the shortlisted vendors, especially those in similar industries or with similar business models. Ask about implementation challenges, support quality, and actual ROI.
- Negotiation & Contract Review: Understand the licensing model (per-user, tiered), storage limits, support costs, and any hidden fees. Don’t overlook implementation services, which can be a significant cost.
- Implementation & Training Planning: The purchase is just the beginning. Develop a clear implementation plan, allocate internal resources, and prioritize comprehensive user training. User adoption is the single biggest factor in CRM success or failure.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Buying Based on Features, Not Needs: Don’t get distracted by a long list of features you’ll never use. Focus on capabilities that solve your immediate and foreseeable problems.
- Underestimating Implementation: CRM implementation is a project, not just an installation. It requires data migration, customization, process re-engineering, and significant internal resources.
- Neglecting User Adoption: The best CRM in the world is useless if your team doesn’t use it. Involve users from day one, provide thorough training, and highlight “what’s in it for them.”
- Ignoring Data Quality: “Garbage in, garbage out.” Prioritize data cleansing and migration from legacy systems. Poor data quality will undermine all CRM efforts.
- Choosing Solely on Price: The cheapest CRM might end up being the most expensive if it doesn’t meet your needs, requires extensive workarounds, or lacks proper support. Value is a balance of cost and capability.
By approaching CRM selection strategically and with a clear understanding of your organizational needs, you lay a robust foundation for improved customer relationships and sustainable business growth.
CRM vs. Marketing Automation: Distinct Roles & Integrated Power
| Aspect | CRM Focus | Marketing Automation Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Manage and nurture existing customer relationships | Attract, qualify, and convert new leads |
| Core Functionality | Contact management, sales pipeline, customer service, support | Lead nurturing, email campaigns, landing pages, lead scoring, analytics |
| Main User Teams | Sales, Customer Service, Account Management | Marketing Team |
| Key Data Tracked | Customer interaction history, purchase data, support tickets | Website visits, email opens, content downloads, lead behavior |
| Impact on Customer Journey | Retention, Upsell, Loyalty (Post-Conversion) | Awareness, Consideration, Conversion (Pre-Conversion) |
- CRM Demo Guide: Choosing the Best CRM for Your Business
- Understanding CRM Systems: A Guide to Customer Relationship Management
- Top B2B CRM Software for Business Growth
- Best Cloud CRM Solutions for Small Businesses in 2024
- Top B2B CRM Software Solutions for Growth
- Best Cloud CRM Solutions for Small Businesses
- Customer Experience Management: Tools and Strategies
- CRM Cloud Solutions: The Future of Customer Relationship Management
- Top Candidate Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Top Enterprise CRM Software: Streamlining Operations
Specific CRM Platform Guides

Navigating the vast ecosystem of CRM platforms can be daunting. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution; the “best” CRM is the one that perfectly aligns with your specific business processes, team size, budget, and future growth objectives. Remember, the global CRM software market continues its robust growth, with Gartner forecasting worldwide end-user spending on customer experience and relationship management (CRM) software to reach $103 billion in 2024. This signifies both massive innovation and significant complexity in choice. Below, we’ve broken down some of the leading platforms, highlighting their strengths, ideal use cases, and critical considerations from a practitioner’s perspective.
Salesforce Sales Cloud
Best For: Enterprise-level organizations, rapidly scaling companies, and businesses requiring extensive customization, deep integrations, and a robust ecosystem of third-party applications. If your sales process is complex and you need granular control over every aspect of the customer journey, Salesforce Sales Cloud is often the gold standard.
- Key Features & Strengths:
- Unparalleled Customization: Almost every aspect can be configured to match unique workflows, reporting needs, and data models.
- Vast Ecosystem (AppExchange): A marketplace with thousands of apps, extending functionality across virtually any business function.
- Scalability: Designed to grow with your business, from a few users to tens of thousands.
- AI Capabilities (Einstein): Predictive analytics, lead scoring, and automated insights.
- Market Leadership: Continual innovation and strong community support.
- Considerations & Common Pitfalls:
- Cost: Can be significantly more expensive than competitors, especially as you add users, features, and custom development. Licensing tiers require careful planning.
- Complexity: Requires dedicated administrators or consultants for setup, ongoing maintenance, and advanced customization. Not a plug-and-play solution.
- User Adoption: Its vastness can be overwhelming for new users without proper training and change management.
- Implementation Time: Expect longer implementation cycles compared to simpler CRMs.
- Practitioner’s Pro-Tip: Don’t try to implement every possible feature on day one. Start with your core sales process, optimize that, and then gradually introduce advanced functionalities. Over-licensing or over-customizing too early is a common, expensive mistake. Focus on driving user adoption through simplicity initially.
HubSpot CRM Suite (Sales Hub, Marketing Hub, Service Hub)
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and mid-market companies that are heavily invested in the inbound methodology. It’s ideal for those seeking an all-in-one platform for sales, marketing, and customer service that prioritizes ease of use and integrated workflows.
- Key Features & Strengths:
- Ease of Use: Intuitive interface makes it quick for sales and marketing teams to get started.
- Integrated Hubs: Seamlessly connects marketing automation, sales pipeline management, and customer service tools within a single platform.
- Strong Inbound Focus: Excellent tools for content creation, SEO, social media, email marketing, and lead nurturing.
- Free CRM Option: A powerful free tier makes it accessible for startups or those testing the waters.
- Robust Reporting: User-friendly dashboards and analytics across all functions.
- Considerations & Common Pitfalls:
- Scaling Costs: While the free CRM is compelling, costs can escalate rapidly as you add contacts, users, and move up to higher-tiered Marketing, Sales, or Service Hubs.
- Customization Limits: Less flexible for highly complex, bespoke sales processes compared to platforms like Salesforce.
- Feature Depth: While broad, individual feature depth may not match best-of-breed, standalone tools for very niche requirements (e.g., highly advanced ABM strategies).
- Pricing Model: Contact-based pricing for marketing automation can lead to unexpected costs if your database grows quickly.
- Practitioner’s Pro-Tip: Leverage the free CRM to its fullest, then strategically upgrade as your needs evolve. Be mindful of your contact database size and how it impacts your monthly spend on Marketing Hub. Implement a strict data hygiene policy from day one to avoid paying for junk leads.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales
Best For: Enterprises and large organizations that are already heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem (e.g., Office 365, Azure, Power BI). It’s a strong choice for businesses that value deep integration with their existing Microsoft software and require a robust, scalable CRM solution.
- Key Features & Strengths:
- Seamless Microsoft Integration: Deep connectivity with Outlook, Teams, Power BI, and other Microsoft applications.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Available on-premises or in the cloud (Microsoft’s Azure cloud).
- Scalability & Extensibility: Highly customizable and scalable for large, complex organizations.
- Power Platform Integration: Leverage Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI for bespoke applications and workflows without extensive coding.
- Global Reach: Backed by Microsoft’s global data centers and support infrastructure.
- Considerations & Common Pitfalls:
- Complexity: Like Salesforce, it can be complex to configure and manage, often requiring specialized IT resources or partners.
- User Interface: Can feel less intuitive or modern to some users compared to competitors, requiring more training.
- Licensing Complexity: Microsoft’s licensing can be intricate, with various modules and add-ons impacting costs.
- Implementation Cost & Time: Significant investment in implementation and ongoing support is often required.
- Practitioner’s Pro-Tip: If you’re a Microsoft-centric organization, maximize the integration capabilities. Don’t simply port your old processes; use Dynamics 365 as an opportunity to streamline workflows by leveraging its native connectivity with your existing Microsoft tools. Invest in robust user training to overcome initial adoption hurdles.
Zoho CRM
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses and startups looking for a comprehensive, cost-effective CRM solution that can scale. It’s particularly attractive to companies wanting an integrated suite of business applications from a single vendor, covering sales, marketing, finance, and more.
- Key Features & Strengths:
- Affordability: Offers competitive pricing across its various tiers, making it accessible for budget-conscious organizations.
- Comprehensive Suite: Part of the larger Zoho One ecosystem, providing a vast array of integrated business applications beyond just CRM (e.g., marketing automation, finance, HR, project management).
- Ease of Setup (for core functions): Relatively straightforward to set up for basic CRM needs.
- Customization (within limits): Allows for a good degree of customization for fields, layouts, and workflows.
- Mobile App: Solid mobile experience for on-the-go sales teams.
- Considerations & Common Pitfalls:
- User Interface: While functional, some users may find the UI less polished or modern compared to HubSpot or Salesforce.
- Scalability for Enterprise: While robust for SMBs, large enterprises with highly complex, unique requirements might find its depth less than Salesforce or Dynamics.
- Support: While improving, customer support experiences can vary, sometimes requiring patience for complex issues.
- Feature Overload (Zoho One): The sheer number of applications in the full Zoho One suite can be overwhelming for teams if not introduced strategically.
- Practitioner’s Pro-Tip: Explore the full Zoho One suite if you’re looking to consolidate multiple business applications under one vendor. This can provide significant cost savings and streamlined data flow. However, implement in phases. Don’t attempt to roll out 10 new Zoho apps simultaneously; focus on CRM first, then gradually introduce others as your team becomes comfortable.
- Green Forest CRM: Streamlining Business Operations
- Datto Autotask PSA: CRM Features for Service Businesses
- Zoho CRM Download & Setup: A Complete Guide
- HubSpot vs. Salesforce CRM: A Demo Comparison
- Kent CRM: Features, Benefits, and How to Get Started
- Salesforce Dreamforce 2024: Key Takeaways & Trends
- Salesforce in Gartner Magic Quadrant: A CRM Leader
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM: Maximizing Sales Performance
- Oracle Sales Automation: Streamline Sales Processes
- Perfex CRM: Features, Demo, and Free Download
CRM & Marketing Automation Features & Best Practices

Implementing CRM and Marketing Automation effectively hinges on understanding not just the features available, but how to deploy them with best practices to maximize impact. This isn’t about simply checking boxes; it’s about building a cohesive, efficient, and customer-centric operation.
Centralized Customer Data & Contact Management
At the core of any powerful CRM and marketing automation strategy is a robust system for managing customer data. This is your single source of truth.
- Unified Contact Profiles: Go beyond basic contact details. A best practice is to aggregate all interactions – emails sent, web pages visited, support tickets, sales calls, purchase history – into a single, comprehensive profile. Tools like Salesforce Sales Cloud, HubSpot CRM, and Zoho CRM excel at this, providing a 360-degree view of the customer.
- Granular Segmentation: Don’t just segment by demographics. Best practice dictates dynamic segmentation based on behavior (e.g., website activity, email engagement), purchase history, lead score, and lifecycle stage. This enables hyper-targeted campaigns. For instance, identify “highly engaged leads who viewed pricing page but haven’t requested a demo.”
- Data Hygiene & Enrichment: This is a non-negotiable. Bad data yields bad insights and poor personalization. Implement regular data cleansing protocols (e.g., duplicate removal, invalid email detection). Consider data enrichment services to add valuable firmographic or technographic details to existing records, making your segmentation even more powerful.
- Activity Logging & Task Automation: Ensure every sales and service interaction is logged automatically or manually. Automate follow-up tasks based on specific triggers (e.g., “send welcome email 5 minutes after sign-up,” “create task for sales rep if lead score exceeds X”).
- Non-Obvious Insight: The true power of a unified data view isn’t just for sales or marketing; it transforms customer service. When a support agent can see the full marketing and sales journey, they can offer more empathetic and efficient solutions, turning a potential complaint into a loyalty builder.
- Salesforce in Gartner Magic Quadrant: A CRM Leader
- SAP CRM Modules: A Guide to Business Optimization
- SuiteCRM Marketing Automation: Features & Benefits
- Customer Data Platforms: Salesforce and Beyond
- Automated Customer Segmentation Software: Target Your Marketing
- Zoho Marketing Automation: Pricing, Features, and CRM Integration
- Free Microsoft CRM Options for Small Businesses
- Free Real Estate CRM Software: Manage Clients on a Budget
Lead Management & Sales Pipeline Automation
Moving leads efficiently from awareness to conversion requires a well-defined process, supported by intelligent automation.
- Lead Scoring & Grading: Implement a clear lead scoring model that assigns points based on explicit data (e.g., job title, company size) and implicit data (e.g., website visits, email clicks). Best practice involves regular calibration of these scores with your sales team to ensure accuracy and alignment with sales-qualified leads (SQLs). Tools like HubSpot Marketing Hub, Marketo Engage (Adobe), and Pardot (Salesforce Marketing Cloud Account Engagement) offer robust lead scoring capabilities.
- Automated Lead Nurturing Workflows: Design multi-stage, branching workflows that respond to lead behavior. If a lead clicks on a pricing page, send a case study. If they download an eBook, send related content. Use decision logic (IF/THEN statements) to personalize the journey.
- Lead Routing & Assignment: Automate the immediate assignment of qualified leads to the correct sales rep based on criteria like geography, industry, or company size. This minimizes response time, a critical factor in lead conversion. Pipedrive and CRM modules within Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics 365 have strong routing capabilities.
- Pipeline Visualization & Management: Ensure your CRM provides a clear, visual representation of your sales pipeline (e.g., Kanban view). This allows sales managers to quickly identify bottlenecks, forecast revenue, and coach reps effectively. Automate updates to deal stages based on completed activities (e.g., “deal moves to ‘Proposal Sent’ stage after proposal email is sent”).
- Non-Obvious Insight: Avoid “lazy” lead scoring. Don’t just assign points; regularly review which actions actually predict conversion with your sales team. A lead that visits your “Careers” page might look active, but it’s not a buying signal. Refine your model based on closed-won deals, not just general engagement.
Marketing Campaign Automation & Personalization
Beyond basic email blasts, marketing automation enables sophisticated, multi-channel customer journeys.
- Multi-Channel Campaign Orchestration: Don’t limit automation to email. Best practice includes integrating SMS, social media posting, retargeting ads, live chat prompts, and even direct mail into your automated workflows. For example, if a cart is abandoned, send an email, then an SMS, then trigger a targeted ad on social media. Platforms like ActiveCampaign and HubSpot are strong in this area.
- Dynamic Content & Hyper-Personalization: Move beyond just using a recipient’s first name. Leverage all available data points (industry, role, past purchases, viewed products) to dynamically alter images, text blocks, and calls-to-action within emails and landing pages. This level of personalization significantly boosts engagement.
- A/B Testing & Optimization: Continuously test subject lines, email content, landing page layouts, and calls-to-action within your automated campaigns. Small iterative improvements compound over time. Automate split testing within your platforms and let the data guide your optimizations.
- Landing Page & Form Builders: Utilize integrated tools to quickly create optimized landing pages and forms that feed directly into your CRM. This ensures lead data is captured accurately and immediately enters your automated workflows.
- Non-Obvious Insight: The most common mistake is automating bad processes. Before automating, meticulously map out your ideal customer journeys for different segments and stages. Understand the user’s intent and pain points at each touchpoint. Automation should amplify a well-thought-out strategy, not merely digitize existing chaos.
Analytics, Reporting & ROI Measurement
You can’t optimize what you can’t measure. Robust analytics are crucial for proving value and identifying areas for improvement.
- Customizable Dashboards & Reports: Create dashboards tailored to different roles (e.g., marketing manager, sales rep, executive). Track key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to your goals, such as lead-to-MQL conversion rates, MQL-to-SQL rates, sales cycle length, and campaign ROI.
- Closed-Loop Reporting: This is paramount. Ensure your CRM and marketing automation platforms are integrated to track the entire customer journey, from initial marketing touchpoint to closed-won deal. This allows you to attribute revenue back to specific marketing campaigns and channels. Platforms like HubSpot are built with closed-loop reporting in mind, while Salesforce Marketing Cloud and Pardot integrate seamlessly with Sales Cloud.
- Attribution Modeling: Go beyond “first touch” or “last touch.” Experiment with multi-touch attribution models (e.g., linear, time decay, W-shaped) to understand the true impact of various marketing activities throughout the customer journey.
- Sales Forecasting & Pipeline Health: Leverage the data within your CRM to generate accurate sales forecasts and identify potential issues in your pipeline (e.g., too many deals stuck in one stage).
- Non-Obvious Insight: Many organizations track activity (emails sent, clicks) but fail to connect these activities directly to business outcomes like revenue. Focus relentlessly on revenue attribution. If you can’t demonstrate how your automation efforts contribute to the bottom line, your team will struggle to justify continued investment.
Integrations & Ecosystem Management
Your CRM and marketing automation platforms are rarely standalone; they’re part of a broader tech stack.
- Strategic Integration Planning: Before connecting anything, map out your entire tech stack (ERP, customer service, billing, accounting, webinar platforms, social media tools). Identify which systems need to share data and for what purpose. Prioritize integrations based on business impact.
- Leveraging Native Integrations: Always check for pre-built, native integrations first. These are typically more robust, easier to set up, and maintained by the software vendors. For example, Salesforce has a vast AppExchange, and HubSpot has a strong App Marketplace.
- Utilizing iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) Tools: For custom or complex integrations where native options are insufficient, use iPaaS solutions like Zapier (for simpler workflows), Workato, or Mulesoft (for enterprise-level needs). These platforms enable data synchronization and workflow automation across disparate systems without extensive custom coding.
- Data Synchronization Protocols: Define how data will sync (one-way vs. two-way), frequency, and conflict resolution rules. Inconsistent data across systems can negate all the benefits of integration.
- Non-Obvious Insight: Beware the “integration tax.” Poorly planned integrations lead to data silos, manual workarounds, and a fragmented customer experience. A robust integration strategy is an ongoing commitment, requiring regular review and maintenance, not a one-time setup. Prioritize data quality and consistency across all connected systems above all else.
- Boost Salesforce Email Marketing: Automation & Best Practices
- Mastering Salesforce Lists: Creation, Management & Best Practices
- Top ActiveCampaign CRM Features: Enhance Your Customer Management
- Real-Time Business Insights: CRM & Salesforce Updates
- Effective CRM Dashboards: A Guide to Data Visualization
- CRM Automation for Follow-Ups: Never Miss a Lead
- ActiveCampaign CRM Features: A Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering Calendars in Semrush, CRM, and Pipedrive
- HubSpot Social Media Management: Features and Benefits
- Master ActiveCampaign: Unlock its Power for Your Business
Marketing Automation Strategies & Implementation
Marketing automation isn’t just about sending emails; it’s a strategic imperative that transforms how businesses engage with prospects and customers at scale. It’s about leveraging technology to deliver the right message to the right person at the right time, freeing up your team to focus on high-value interactions. This section delves into the actionable strategies and a robust implementation framework you need to succeed.
Laying the Strategic Foundation: More Than Just Tools
Before you even think about software, you must define your marketing automation strategy. This isn’t a technical exercise; it’s a business one. Your strategy should align directly with overarching business goals, whether that’s lead generation, customer retention, or increasing average customer lifetime value (CLTV).
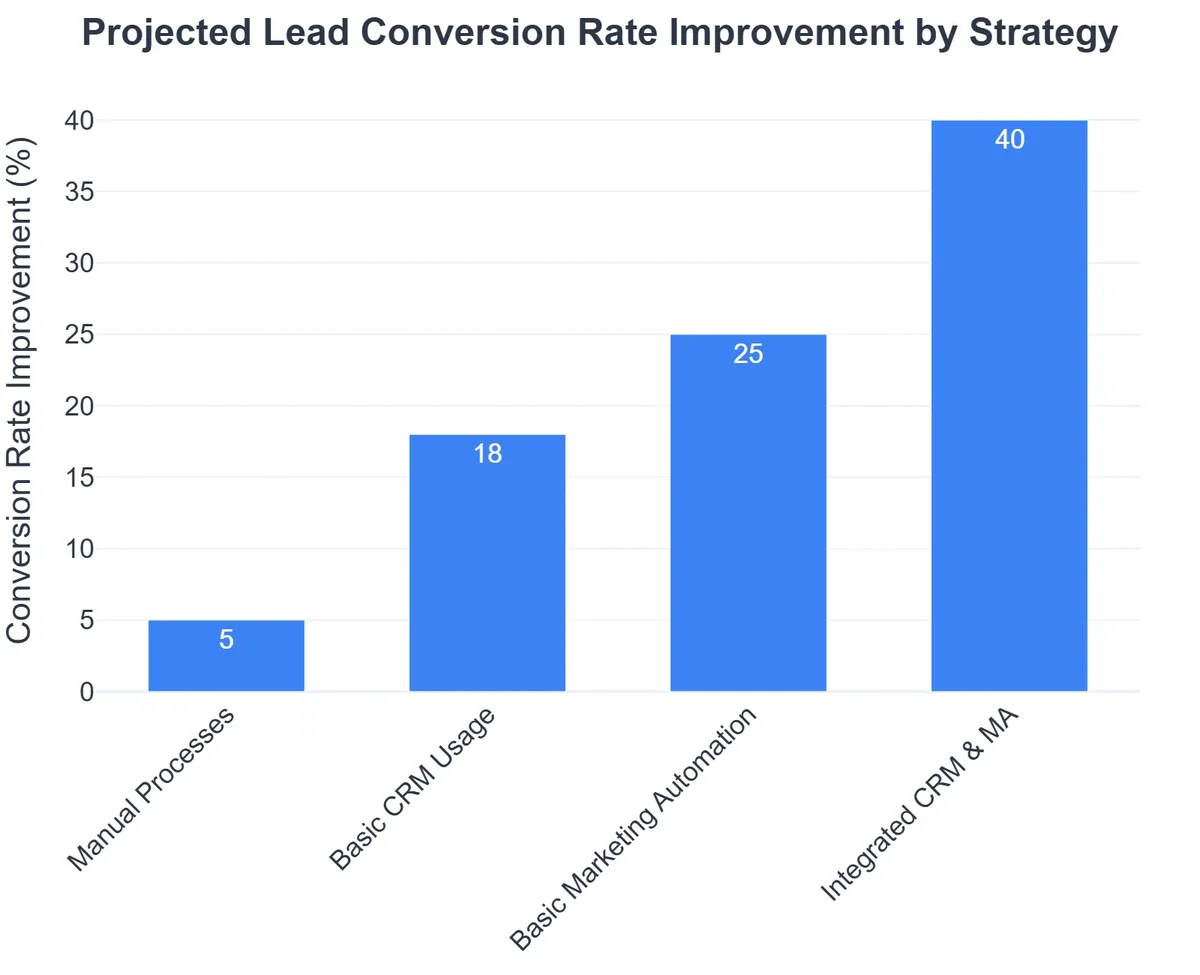
- Define Clear Objectives & KPIs: What do you want to achieve? Is it a 15% increase in MQL-to-SQL conversion? A 10% reduction in customer churn? Without concrete, measurable goals (Key Performance Indicators or KPIs), your efforts will lack direction.
- Audience Segmentation Mastery: Generic campaigns fail. Your audience is not a monolith. Develop detailed buyer personas and segment your audience based on demographics, psychographics, behavior (e.g., website visits, past purchases), and their position in the buyer journey. Tools like Salesforce Marketing Cloud, HubSpot, and ActiveCampaign offer sophisticated segmentation capabilities.
- Map the Customer Journey: Visualizing the end-to-end customer journey from awareness to advocacy is critical. Identify key touchpoints and potential friction points. For each stage, determine what information the prospect needs, what actions you want them to take, and what content will resonate most effectively.
- Content Strategy Alignment: Marketing automation is merely the delivery mechanism for your content. You need a robust content strategy that provides relevant, valuable content for each segment and journey stage. This includes blog posts, whitepapers, case studies, videos, webinars, and more.
- CRM as the Single Source of Truth: Your marketing automation platform must integrate seamlessly with your CRM system (e.g., Salesforce Sales Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Zoho CRM). The CRM provides the foundational data for segmentation and personalization, ensuring a unified view of the customer across sales, marketing, and service. This integration is non-negotiable for a truly holistic approach.
- Marketo Nurture Campaigns: Driving Engagement with Adobe Campaign
- Boost Engagement with Creative Marketing Automation
Selecting Your Marketing Automation Powerhouse
The market is saturated with platforms, each with its strengths. Your choice will depend on your business size, complexity, budget, and specific needs. Do not over-buy or under-buy.
- Enterprise Solutions: For large organizations with complex needs, deep integration requirements, and significant budgets, consider platforms like Salesforce Marketing Cloud (Pardot/Account Engagement), Marketo Engage (Adobe), or Oracle Eloqua. These offer extensive customization, advanced analytics, and robust APIs.
- Mid-Market & Scalable Growth: For growing businesses needing a powerful yet intuitive solution, HubSpot (with its all-in-one CRM suite) and ActiveCampaign are strong contenders. Braze is excellent for mobile-first engagement, while Klaviyo dominates the e-commerce marketing automation space with its deep Shopify and Magento integrations.
- SMB & Budget-Conscious: Solutions like MailerLite (for simpler needs), Sendinblue (Brevo), and integrated CRM suites like Zoho CRM Plus offer great value, combining email marketing with basic automation, landing pages, and CRM functionalities.
- Key Selection Criteria: Always evaluate based on ease of use, integration capabilities (especially with your CRM), scalability, reporting and analytics, customer support, and, critically, security and compliance features (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
The Implementation Playbook: From Concept to Campaign
Once your strategy is clear and your platform is chosen, follow a structured implementation process. This isn’t a one-time setup; it’s an iterative process of build, test, launch, and optimize.
- Data Cleanse & Migration: This is often overlooked but absolutely critical. Poor data quality will cripple your automation efforts. Clean, de-duplicate, and standardize your existing contact data. Map fields meticulously between your CRM and MA platform during migration. Garbage in, garbage out applies tenfold here.
- Integrate Your Ecosystem: Connect your marketing automation platform to your CRM, website, landing page builder, webinar platforms, and any other relevant tools. API integrations and native connectors are key. Ensure data flows bidirectionally and in real-time where necessary.
- Define & Build Automation Workflows (Journeys): This is the core. For each customer journey stage (e.g., Lead Nurturing, Onboarding, Re-engagement, Upsell), design specific workflows.
- Entry Triggers: What action initiates the journey? (e.g., form submission, product view, specific page visit, abandoned cart).
- Conditional Logic: Use “if/then” statements to personalize paths (e.g., “If they opened email X, send email Y; else, send email Z”).
- Actions: Define what the system does (send email, SMS, push notification, update CRM field, assign lead to sales, add to a different list).
- Exits: What signals the end of the journey for a contact? (e.g., purchase, unsubscribe, form submission for a sales call).
- Time Delays: Strategically space out communications to avoid overwhelming prospects.
Non-Obvious Insight: Don’t try to automate everything at once. Start with one or two critical, high-impact journeys (e.g., new lead nurturing or abandoned cart recovery) and expand incrementally.
- Develop Personalization & Dynamic Content: Leverage the data in your CRM to personalize content beyond just “first name.” Use dynamic content blocks to display different offers, product recommendations, or messages based on segmentation rules. Tools like HubSpot’s Smart Content or Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s AMPscript enable this.
- Set Up Scoring Models: Implement lead scoring (for leads) and engagement scoring (for customers). Assign points based on behaviors (e.g., website visits, content downloads, email opens) and demographic data. This helps sales prioritize hot leads and marketing identify at-risk customers. Regularly review and adjust your scoring rules.
- Thorough Testing: Before going live, test every single workflow, email, landing page, and integration point. Send test emails to various clients (desktop, mobile). Check all links, personalization tokens, and conditional logic. Test lead scoring to ensure leads are scored correctly.
- Launch & Monitor: Once everything is tested, launch your campaigns. But the work isn’t over. Actively monitor performance in real-time. Look for bottlenecks, unexpected drops in engagement, or technical glitches.
- Optimize & Refine Continuously: Marketing automation is not “set it and forget it.”
- A/B Test: Always A/B test subject lines, email body copy, calls-to-action (CTAs), and even timing.
- Analyze Metrics: Dive deep into open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, unsubscribe rates, and ultimately, ROI. Use the built-in analytics dashboards of platforms like Marketo Engage or Klaviyo.
- Iterate: Use data insights to refine your segments, tweak your workflows, improve your content, and adjust your scoring models. This continuous feedback loop is what drives long-term success.
Common Pitfall: Many organizations implement automation and then fail to iterate. Without continuous optimization based on performance data, your campaigns will quickly become stale and inefficient.
- Automated Marketing Workflows: Design & Implementation Guide
- Automated Marketing Workflows: A Practical Guide
- Digital Lead Nurturing: Strategies for Effective Lead Management
- Marketing Automation Triggers: A Complete Guide
- Sales & Marketing Alignment: A Guide to Business Growth
- Marketing & Sales Alignment: A Growth Strategy Guide
- Strategic Planning for CRM and E-marketing Success
- Affordable Marketing Automation: Low-Cost Solution Guide
- Simple Marketing Automation: A Beginner’s Guide
- Smartsheet Email Automation: Streamline Your Workflow
Integrations & Workflow Optimization

The true power of CRM and Marketing Automation platforms isn’t just in their individual capabilities, but in their ability to communicate seamlessly with each other and with the broader technology stack of your organization. This interconnectedness is the cornerstone of a unified customer experience and operational efficiency. Without robust integrations, even the most sophisticated tools become isolated data silos, leading to disjointed customer journeys, manual data entry, and missed opportunities.
The Imperative of Integration: Breaking Down Data Silos
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, customers expect personalized, coherent interactions across every touchpoint. This is impossible when customer data is fragmented across disparate systems. Integration serves as the crucial bridge, enabling a holistic 360-degree view of the customer. Consider a scenario where your marketing team is nurturing a lead, but sales isn’t aware of their engagement history, or customer support doesn’t know about their recent purchase intent. Integrations eliminate these blind spots, leading to:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Consistent messaging and proactive support.
- Increased Efficiency: Automating data transfer reduces manual effort and errors.
- Superior Data Accuracy: A single source of truth minimizes discrepancies.
- Advanced Analytics: Correlating data across departments for deeper insights.
- Faster Response Times: Real-time information empowers timely actions.
- Mautic Social Media Integration: Amplify Your Marketing Reach
- HubSpot & Salesforce Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
- SugarCRM Integration Strategies: Boost Business Efficiency
- CMS & CRM Integration for Marketing Success
- Pipedrive Integrations: Connect Sales & Marketing Tools
- 360 View CRM & Salesforce Integration: Benefits Explained
Types of Integration Architectures: Choosing Your Path
Not all integrations are created equal. Understanding the different approaches is critical to selecting the right strategy for your organization’s needs and resources.
1. Native/Out-of-the-Box Integrations
- Description: Pre-built connectors provided by software vendors. These are typically the easiest to set up and maintain.
- Examples: Salesforce with Pardot (both Salesforce products), HubSpot CRM with HubSpot Marketing Hub, Microsoft Dynamics 365 with other Microsoft applications. Often, a CRM will have native integrations with popular apps like Mailchimp, Zoom, or common accounting software.
- Pros: Simple setup, often well-documented, vendor-supported.
- Cons: Limited customization, may not cover all your specific use cases.
2. API-based/Custom Integrations
- Description: Building bespoke connections between systems using their Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This requires significant development resources.
- Examples: Connecting a legacy ERP system (e.g., an older version of SAP or a highly customized Oracle E-Business Suite) to a modern cloud CRM like Salesforce, or integrating a proprietary customer database with a marketing automation platform.
- Pros: Maximum flexibility and control, tailored to exact business logic.
- Cons: High development cost, requires skilled developers, ongoing maintenance burden, slower to implement.
3. iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service)
- Description: Cloud-based platforms that provide tools and connectors to build, deploy, and manage integrations between applications without extensive coding. They act as a middleware layer.
- Examples: Zapier (great for simpler, event-driven integrations), Workato, MuleSoft Anypoint Platform, Dell Boomi, Tray.io. These platforms often boast thousands of pre-built connectors and visual workflow builders.
- Pros: Faster development cycles, less reliance on custom code, scalability, centralized monitoring, often low-code/no-code.
- Cons: Subscription costs, potential vendor lock-in, may not handle extremely complex, high-volume batch integrations as efficiently as custom solutions or enterprise ESBs (Enterprise Service Buses).
Core Systems Requiring Integration for Workflow Optimization
To achieve a truly optimized workflow, your CRM and Marketing Automation platforms must seamlessly interact with a range of other critical business systems:
- CRM & Marketing Automation: (The fundamental link).
- Purpose: Sync leads, contacts, activities, lead scores, campaign memberships, and marketing qualified lead (MQL) status. This ensures sales has full visibility into marketing engagement and vice-versa for effective lead nurturing and handoff.
- Example Workflow: A lead fills out a form on your website (captured by MA), is scored based on their behavior (MA), reaches MQL status (MA), then automatically creates an opportunity in CRM, alerting the sales rep. Sales activities in CRM (calls, meetings) can then inform lead scoring or segment triggers in MA.
- CRM/MA & Customer Support/Service:
- Purpose: Provide support agents with customer context (purchase history, marketing interactions) and feed customer service data (support tickets, resolutions) back into CRM for a complete customer view.
- Tools: Zendesk, ServiceNow, Salesforce Service Cloud.
- Example Workflow: A customer submits a support ticket via Zendesk. This ticket is automatically linked to their contact record in Salesforce. If the issue is critical or persistent, it could trigger an automated task for their account manager in CRM or segment them for specific follow-up communication in MA.
- CRM/MA & ERP/Financial Systems:
- Purpose: Link customer records with order history, billing, inventory, and fulfillment data. Crucial for understanding customer lifetime value (CLTV) and automating order-related communications.
- Tools: SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations, QuickBooks Online.
- Example Workflow: An order is placed in NetSuite. This triggers an automated post-purchase email series from the marketing automation platform (e.g., shipping updates, product usage tips), and updates the customer’s purchase history in HubSpot CRM.
- CRM/MA & Data Warehouses/Business Intelligence (BI) Tools:
- Purpose: Aggregate data from all systems into a centralized repository for advanced analytics, reporting, and strategic decision-making.
- Tools: Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Looker.
- Example Workflow: Sales, marketing, and support data is funneled into Snowflake. A BI analyst uses Tableau to visualize the entire customer journey, identify churn risks, or pinpoint successful marketing campaigns based on revenue attribution.
- CRM/MA & Communication/Collaboration Tools:
- Purpose: Streamline internal communications related to customer activities.
- Tools: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Asana, Jira.
- Example Workflow: When a high-value lead engages with specific content or a customer submits a critical support ticket, an automated alert is sent to the relevant team’s Slack channel, ensuring immediate awareness and action.
Workflow Optimization in Action: Practical Scenarios
Let’s look at concrete examples of how integrations drive optimized workflows:
Scenario 1: Automated Lead Management & Handoff
- The Problem: Manual lead qualification, slow sales follow-up, leads falling through the cracks.
- The Solution: Integrate HubSpot Marketing Hub (MA) with Salesforce Sales Cloud (CRM).
- Marketing captures leads, nurtures them through email sequences, and assigns a lead score.
- Once a lead reaches a predefined MQL threshold (e.g., score > 75), HubSpot automatically creates a new Lead record or converts an existing Contact in Salesforce.
- Salesforce then automatically assigns the lead to the appropriate sales rep based on territory or other rules, creates a follow-up task, and sends a notification via Slack to the rep.
- Result: Faster lead response, improved conversion rates, transparent lead lifecycle.
Scenario 2: Personalized Post-Purchase Journey & Upsell Opportunities
- The Problem: Generic post-purchase communication, missed opportunities for repeat business.
- The Solution: Integrate your E-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, Magento) with Marketo (MA) and your CRM (e.g., Salesforce or Dynamics 365).
- When a customer completes a purchase on Shopify, the order details are pushed to Marketo and the CRM.
- Marketo triggers a personalized “thank you” email series, product usage tips, and satisfaction surveys based on the purchased items.
- If the customer’s purchase behavior (e.g., buying related accessories) or survey responses indicate interest in an upgrade, Marketo can update their CRM record and trigger an upsell campaign or task for a sales rep.
- Result: Higher customer satisfaction, reduced churn, increased customer lifetime value.
Scenario 3: Proactive Customer Service & Feedback Loop
- The Problem: Customer issues are reactive, support agents lack context, customer feedback isn’t utilized.
- The Solution: Integrate Salesforce Service Cloud (CRM/Service) with Gainsight (CSM) and Qualtrics (Survey Platform).
- A customer submits a critical support ticket in Service Cloud.
- The ticket details automatically update the customer’s health score in Gainsight. If the score drops below a threshold, it triggers an alert to the Customer Success Manager (CSM) and creates a proactive outreach task.
- After the ticket is resolved, a satisfaction survey is automatically sent via Qualtrics. The survey results are pushed back into Service Cloud and Gainsight, providing valuable insights for future product development and service improvements.
- Result: Improved customer retention, better product development, enhanced service quality.
Advanced Strategies & Common Pitfalls
Achieving truly optimal integrations goes beyond simply connecting systems. Consider these advanced strategies and avoid common traps:
1. Data Strategy First, Integration Second
Non-Obvious Insight: Don’t jump into buying iPaaS solutions or building custom APIs until you have a clear data strategy. Map out your data flows: what data lives where, what is the single source of truth for each data point (e.g., customer name, purchase history), how does it transform, and where does it need to go? A well-defined data model and governance plan prevent “garbage in, garbage out” scenarios.
2. Embrace “Reverse ETL”
Non-Obvious Insight: While traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) moves data into a data warehouse for analytics, “Reverse ETL” is the process of moving transformed, enriched data back into operational systems like CRM, Marketing Automation, or ERP. This operationalizes your insights.
- Example: Your data warehouse (e.g., Snowflake) combines customer data with product usage data, support tickets, and web analytics to identify your “most at-risk customers.” Instead of just reporting this, Reverse ETL pushes this “at-risk” flag directly back into Salesforce CRM, allowing account managers to proactively intervene. Tools like Census and Hightouch specialize in Reverse ETL.
3. Plan for Scalability and Future-Proofing
Avoid point-to-point integrations for every new tool. This creates a “spaghetti architecture” that becomes brittle and unmanageable. An iPaaS solution or a well-architected API layer provides a more robust and scalable foundation for growth. Think about how your integration strategy will handle new tools, increased data volume, and evolving business requirements.
4. Don’t Neglect Data Hygiene and Governance
Integrations will highlight existing data quality issues. Implement robust data cleansing, deduplication, and validation processes both before and during integration. Define clear data ownership and governance rules to maintain data integrity across all connected systems.
5. Test, Monitor, and Iterate Constantly
Integrations are not a “set it and forget it” solution. Changes in one system’s API, data structure, or business logic can break integrations. Implement automated testing, continuous monitoring (e.g., using tools like Datadog for API monitoring or built-in iPaaS dashboards), and establish clear protocols for issue resolution. Regular reviews and iterations are key to long-term success.
Mastering integrations is arguably the most critical step in unlocking the full potential of your CRM and marketing automation investments. It transforms individual tools into a cohesive, intelligent ecosystem, directly impacting your bottom line and customer satisfaction.
- Zapier Marketing Automation: Streamline Your Workflows
- Zapier & Eloqua Integration: Automate Your Marketing
- Zoho & HubSpot Integration: Streamline Your Operations
- Integrate Hunter.io, Snov.io, and Reply.io with HubSpot
- Integrate Trustpilot with HubSpot: A Guide to Enhanced Customer Insights
- Seamless Zoho & HubSpot Integration: Unify Your Business Operations
- Connecting Your CRM with Email: A Seamless Integration Guide
- HubSpot & Salesforce Integration: A Complete Review
- Sage 200 CRM Integration with Vultr Cloud
- Integrating Odoo with Mautic & HubSpot: A Marketing Automation Guide
Specific Marketing Automation Platforms

Navigating the vast landscape of marketing automation platforms requires a strategic approach. It’s not about finding the “best” platform, but rather the best fit for your specific business needs, budget, and existing tech stack. Each platform has its unique strengths, ideal use cases, and nuances that practitioners must understand.
Below, we’ll dive into some of the leading platforms, highlighting their core capabilities and providing insights that go beyond the marketing brochures.
HubSpot Marketing Hub
HubSpot pioneered the inbound methodology and its Marketing Hub is a testament to that philosophy. It’s renowned for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive suite of tools designed to attract, engage, and delight customers. It’s often the go-to for companies new to marketing automation or those seeking an all-in-one solution that integrates seamlessly with CRM, sales, and service functions.
- Key Strengths:
- All-in-One Platform: Offers email marketing, landing pages, forms, SEO tools, social media management, blogs, and ad management under one roof.
- Exceptional Usability: Known for its intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, making it accessible even for non-technical users.
- Integrated CRM: The Marketing Hub is built on top of the powerful and free HubSpot CRM, providing a unified view of customer data across all touchpoints.
- Robust Reporting: Comprehensive analytics dashboards that are easy to understand and customize.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- SMBs and Mid-Market Businesses adopting an inbound marketing strategy.
- Companies looking for a single platform solution to manage their entire customer journey.
- Organizations prioritizing ease of use and quick time-to-value.
- Practitioner’s Insight: While HubSpot’s free CRM is excellent, scaling up its Marketing Hub can become significantly more expensive as your contact database grows and you require more advanced features (e.g., custom objects, advanced sequences). Always factor in potential future growth when assessing its long-term cost-effectiveness. The bundled approach is powerful, but ensure you leverage enough of the stack to justify the investment.
Salesforce Marketing Cloud Account Engagement (Pardot)
Formerly known as Pardot, Salesforce Marketing Cloud Account Engagement is Salesforce’s B2B marketing automation solution. It’s specifically designed for companies that rely on the Salesforce CRM and need deep integration for lead nurturing, lead scoring, and sales alignment.
- Key Strengths:
- Deep Salesforce CRM Integration: Unparalleled synergy with Salesforce Sales Cloud, allowing for seamless lead sync, activity tracking, and sales insights.
- Sophisticated Lead Management: Robust lead scoring, grading, and nurturing capabilities that ensure sales teams receive qualified leads.
- Advanced Email Marketing: Powerful email builder with dynamic content and A/B testing.
- Form and Landing Page Builders: Tools to capture leads directly into Salesforce.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- B2B organizations already using Salesforce CRM who want to extend its capabilities with marketing automation.
- Companies with complex sales cycles requiring detailed lead nurturing and scoring.
- Businesses focused on sales-marketing alignment and optimizing the handoff process.
- Practitioner’s Insight: While its integration with Salesforce is a massive advantage, it can also be a challenge. Implementation and optimization often require a certified Pardot/Salesforce consultant due to its complexity and the need for proper configuration within both platforms. Don’t underestimate the setup effort; a poorly integrated Pardot instance can create more problems than it solves. It’s a powerful tool, but it demands expertise.
Adobe Marketo Engage
Adobe Marketo Engage is a robust, enterprise-grade marketing automation platform primarily favored by large B2B organizations and some complex B2C scenarios. It’s known for its extensive feature set, powerful segmentation, and highly customizable automation capabilities, designed for the most intricate customer journeys.
- Key Strengths:
- Enterprise-Level Scalability: Handles massive databases and complex automation flows with ease.
- Unparalleled Customization: Offers immense flexibility for building sophisticated lead nurturing, scoring, and lifecycle programs.
- Advanced Analytics & Attribution: Deep reporting capabilities to measure ROI across various touchpoints.
- Integration Ecosystem: Strong API and marketplace for connecting with a wide range of third-party tools.
- AI-Powered Features: Leverages AI for predictive content, audience segmentation, and lead scoring.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- Large B2B enterprises with long sales cycles and complex customer journeys.
- Organizations requiring highly customized and intricate automation workflows.
- Companies with significant marketing operations teams capable of managing an advanced platform.
- Practitioner’s Insight: Marketo is a “power user” platform. Its strength lies in its flexibility, but this also means a steeper learning curve and a greater need for dedicated resources and skilled operators. It’s not a plug-and-play solution. Misconfigurations or a lack of internal expertise can lead to significant inefficiencies. Ensure your team has the bandwidth and skill set (or budget for experienced consultants) before committing to Marketo.
ActiveCampaign
ActiveCampaign strikes a fantastic balance between power and affordability, making it a compelling choice for small to medium-sized businesses that need sophisticated marketing automation, email marketing, and even basic CRM functionalities. It excels at creating highly personalized customer experiences across multiple channels.
- Key Strengths:
- Advanced Automation Builder: Intuitive drag-and-drop visual automation builder that supports complex conditional logic, branching, and goal tracking.
- Deep Segmentation: Exceptional contact management with extensive tagging and custom field capabilities for hyper-targeted campaigns.
- Multi-Channel Reach: Integrates email, SMS, site messaging, and even a basic CRM for sales pipeline management.
- Strong E-commerce Integrations: Excellent for online stores looking to automate post-purchase flows, abandoned cart sequences, and win-back campaigns.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- SMBs and Mid-Market companies that need robust automation without the enterprise price tag.
- E-commerce businesses looking to personalize customer journeys beyond basic email blasts.
- Service-based businesses requiring sophisticated follow-up and nurture sequences.
- Organizations seeking a highly customizable and flexible platform.
- Practitioner’s Insight: While ActiveCampaign is powerful, its flexibility can sometimes lead to “analysis paralysis” or over-engineering. Start with simpler automations and build complexity incrementally. Also, ensure you have a clear strategy for tagging and segmenting your contacts from day one; a messy contact database will quickly undermine its most powerful features.
Klaviyo
Klaviyo is the undisputed leader in email and SMS marketing automation specifically for e-commerce businesses. It provides highly sophisticated segmentation, personalization, and robust analytics tailored to online sales, making it a crucial tool for driving revenue through owned marketing channels.
CRM & Marketing Automation: Pros and Cons
Pros
- ✔Streamlined customer relationship management.
- ✔Automated lead nurturing and campaign execution.
- ✔Improved data insights for targeted strategies.
- ✔Increased operational efficiency and productivity.
Cons
- ✖Significant initial investment and ongoing costs.
- ✖Complexity in setup, integration, and maintenance.
- ✖Requires dedicated staff training and adoption.
- ✖Potential for impersonal customer interactions if not managed well.
- Key Strengths:
- E-commerce Focus: Built from the ground up for online stores, with native integrations to platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento.
- Deep Data Integration: Easily syncs purchase history, browsing behavior, abandoned carts, and more for hyper-segmentation.
- Powerful Segmentation: Create incredibly precise customer segments based on any data point, leading to highly relevant campaigns.
- Revenue-Centric Reporting: Analytics focus on key e-commerce metrics like revenue generated per email, customer lifetime value, and repurchase rates.
- Predictive Analytics: Offers features like predicted next order date, churn risk, and potential customer lifetime value.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- Any e-commerce business looking to maximize revenue through email and SMS marketing.
- Brands seeking to build strong customer relationships and loyalty through personalized communication.
- Online retailers focused on optimizing customer lifecycle marketing (welcome flows, abandoned carts, post-purchase, win-back).
- Practitioner’s Insight: While Klaviyo is fantastic for e-commerce, it’s less suitable for traditional B2B lead nurturing or service-based businesses not directly tied to product sales. Its power comes from its deep e-commerce data integration. Don’t try to force a square peg into a round hole. For e-commerce, leverage its extensive pre-built flows and constantly A/B test your subject lines, content, and send times. The more data you feed it, the smarter your campaigns become.
- VBOUT Review: Marketing Automation for Shopify & WooCommerce
- IBM Watson Campaign Automation: A Complete Guide
- PrestaShop Marketing Automation: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Mautic & GDPR Compliance: Protecting Your Data
- Monday.com Email Automation: Streamlining Marketing & Sales
- ActiveCampaign Split Automations: A Complete Guide
- Salesmanago Pricing: A Guide to Understanding Your Investment
- Drip CRM: Automate Customer Journeys with Drip Marketing
- GetResponse Marketing Automation: Streamline Your Campaigns
- HubSpot Automation: Power Your Marketing and Sales
Related Business Software & Tools
While CRM and Marketing Automation platforms form the core of your customer-centric operations, they rarely operate in isolation. A truly effective business leverages an integrated ecosystem of software tools to achieve seamless data flow, holistic customer views, and streamlined internal processes. Understanding these related systems is crucial, as their interactions with your CRM and MA platforms determine the efficiency and accuracy of your entire revenue engine.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
For many businesses, particularly those with complex operations involving manufacturing, supply chain, or extensive inventory management, an ERP system is the backbone. While your CRM focuses on customer relationships and sales, the ERP handles the operational side: financials, procurement, inventory, production, and often human resources. Integrations between CRM and ERP are critical for a complete picture of customer activity, from initial lead to order fulfillment and financial reconciliation.
- SAP: A global leader in ERP, particularly for large enterprises, offering comprehensive modules for almost every business function. Integration with CRM ensures sales data flows into operational planning and financial records.
- Oracle NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP solution popular with fast-growing businesses, offering integrated modules for financial management, CRM, e-commerce, and more. Its native SuiteCRM and marketing automation capabilities make it a strong contender for an all-in-one solution for some businesses.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A suite of modular, cloud-based business applications that includes ERP functionalities (Finance, Supply Chain) alongside CRM (Sales, Customer Service, Marketing). It’s designed for seamless integration across its own modules.
- Workday: Primarily known for its human capital management (HCM) and financial management applications, often used by larger organizations that need robust back-office integration.
Practitioner Insight: The most common pitfall is data silos between sales (CRM) and operations/finance (ERP). Ensure your integration strategy allows for bidirectional data flow, so sales has visibility into inventory or order status, and finance has accurate revenue recognition from closed deals. This prevents “finger-pointing” between departments and ensures a consistent customer experience.
Customer Service & Support Platforms
Once a lead becomes a customer, their journey often continues into the service and support realm. These platforms manage customer inquiries, support tickets, knowledge bases, and live chat, serving as the primary touchpoint for post-sales interactions. Integrating them with your CRM provides a 360-degree view of the customer, allowing service agents to see sales history and sales teams to see support interactions.
- Zendesk: A widely adopted cloud-based customer service platform offering ticketing, live chat, self-service portals, and analytics.
- Freshdesk: Another popular helpdesk solution known for its user-friendly interface and robust features for ticket management, automation, and multichannel support.
- Intercom: More than just a support platform, Intercom excels at conversational messaging, offering live chat, chatbots, and targeted email campaigns for customer engagement and support.
- Salesforce Service Cloud: Built on the Salesforce platform, it provides comprehensive service capabilities, leveraging the same customer data as Sales Cloud for a unified view.
Practitioner Insight: Seamless handover between sales and service is paramount. A strong integration ensures that once a deal is closed in CRM, the customer’s profile, purchase history, and any relevant notes are automatically accessible to the service team. This prevents customers from having to repeat themselves and significantly improves satisfaction and retention.
Analytics & Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
Your CRM and Marketing Automation platforms generate vast amounts of data. BI tools are essential for transforming this raw data into actionable insights, dashboards, and reports that inform strategic decisions, identify trends, and measure performance beyond what native reporting offers.
- Tableau: A powerful, highly visual BI tool known for its robust data visualization capabilities and ability to connect to various data sources, including CRMs.
- Microsoft Power BI: Microsoft’s answer to data visualization, offering tight integration with other Microsoft products and strong capabilities for data modeling and reporting. Often a strong choice for businesses already in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Google Looker Studio (formerly Data Studio): A free, web-based tool for creating customizable reports and dashboards, particularly strong for integrating with Google Analytics, Google Ads, and other Google-based data sources, often used to blend marketing performance with CRM sales data.
- Mixpanel and Amplitude: These are more focused on product analytics and user behavior, but their insights into customer engagement within a product can be invaluable when integrated with CRM/MA to understand user journeys and tailor marketing efforts.
Practitioner Insight: Don’t just collect data; visualize it in a way that tells a story. Look for trends across marketing campaigns, sales cycles, and customer service interactions. Leverage BI to identify leading indicators for churn, pinpoint your most profitable customer segments, or uncover which marketing channels truly drive revenue, not just leads.
Accounting & Financial Management Software
The final step in the sales cycle involves invoicing, payments, and revenue recognition. Accounting software handles these critical financial operations. Integration with your CRM ensures that once a deal is closed and won, the necessary financial documents are generated accurately and efficiently.
- QuickBooks: The market leader for small to medium-sized businesses, offering comprehensive accounting features including invoicing, expense tracking, and payroll.
- Xero: A popular cloud-based accounting software, particularly strong for small businesses and known for its user-friendly interface and extensive integrations.
- Sage: Offers a range of accounting and business management software solutions catering to various business sizes, from small businesses to larger enterprises.
- SAP Business One: An integrated ERP solution designed for small to midsize businesses, often covering accounting, CRM, and other core business functions in one system.
Practitioner Insight: Automating the handover from a “Closed-Won” CRM opportunity to an invoice in your accounting system significantly reduces manual errors and accelerates your order-to-cash cycle. This also provides accurate revenue data back into your CRM, completing the sales lifecycle reporting.
E-commerce Platforms
For businesses engaged in online sales, the e-commerce platform is the central hub for transactions. Integrating it with your CRM and Marketing Automation systems allows you to track customer purchases, segment buyers based on their order history, automate post-purchase communications, and personalize marketing efforts.
- Shopify: A leading e-commerce platform, popular for its ease of use and extensive app marketplace, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- WooCommerce: A flexible, open-source e-commerce plugin for WordPress, offering extensive customization options and popular for businesses with existing WordPress websites.
- Magento (Adobe Commerce): A powerful, feature-rich e-commerce platform suitable for large and complex online stores, offering high scalability and customization.
- BigCommerce: A robust cloud-based e-commerce platform known for its comprehensive built-in features and scalability for growing businesses.
Practitioner Insight: Leverage your e-commerce data within your marketing automation to create highly personalized campaigns. Think abandoned cart recovery sequences, post-purchase upsells/cross-sells based on previous purchases, loyalty programs, and re-engagement campaigns for inactive customers. This is where truly targeted marketing happens.
Content Management Systems (CMS) & Website Builders
Your website is often the primary digital storefront and lead generation tool. A CMS allows you to manage website content, forms, and landing pages. Integrating your CMS with CRM and Marketing Automation ensures lead capture forms feed directly into your systems, and website visitor behavior can be tracked to inform segmentation and personalization.
- WordPress: The world’s most popular CMS, highly flexible and extensible with countless plugins and themes, often used with form builders that integrate directly with CRMs.
- Drupal: A robust and highly customizable open-source CMS, often used for complex websites and enterprise-level applications.
- Joomla: Another popular open-source CMS known for its flexibility and community support.
- Wix and Squarespace: User-friendly website builders that offer integrated tools for forms and basic marketing, often with direct integrations or Zapier connections to popular CRMs.
- Adobe Experience Manager (AEM): An enterprise-level CMS solution, part of the Adobe Experience Cloud, offering advanced content management, digital asset management, and personalization capabilities.
Practitioner Insight: Don’t just embed forms; ensure your CRM/MA system is directly tracking website visits and specific page views. This behavioral data provides critical context for lead scoring, segmenting prospects, and personalizing email campaigns based on the content they’ve engaged with on your site.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
As your technology stack grows, managing point-to-point integrations between every system becomes complex and fragile. iPaaS solutions provide a centralized platform to connect disparate applications, automate workflows, and ensure data consistency across your entire ecosystem.
- Zapier: An incredibly popular no-code/low-code integration platform, allowing users to connect thousands of apps with automated “Zaps.” Ideal for smaller, simpler automations between cloud services.
- Make (formerly Integromat): A more powerful and visual automation platform than Zapier, offering more complex logic, branching, and advanced error handling.
- MuleSoft: An enterprise-grade iPaaS solution (now part of Salesforce) designed for complex, high-volume integrations, API management, and hybrid cloud environments.
- Workato: Another enterprise-focused iPaaS platform known for its intelligent automation capabilities and ability to handle sophisticated business processes.
- Boomi: An iPaaS solution (now part of Francisco Partners) known for its robust capabilities in application integration, data integration, and API management.
Practitioner Insight: As your business scales and your tech stack expands, investing in a dedicated iPaaS solution is not just a convenience; it’s a strategic necessity. It prevents integration “spaghetti code,” reduces technical debt, ensures data reliability, and empowers non-developers to build crucial automations, ultimately accelerating your ability to adapt and innovate.
Building a robust and efficient business operation requires more than just excellent CRM and Marketing Automation. It demands a thoughtful approach to how all your systems communicate and share data. By strategically integrating these related software categories, you can create a truly unified customer view, automate critical processes, and unlock powerful insights that drive sustainable growth.
- Zoho Assist & Enterprise Pricing: In-Depth Review
- Salesforce Acquires Tableau: Revolutionizing CRM & BI
- IBM Watson for Marketing: Automating Campaigns and Engagement
- Datto Autotask PSA: CRM Features for Service Businesses
- Smartsheet Email Automation: Streamline Your Workflow
- Airtable as a CRM: A Shopify Store Guide
- Notion CRM: A Complete Guide for Blogging and Newsletters
- Google CRM Tools: A Guide for Business Management
- Field Workforce Management Software: Optimizing Mobile Teams
- Zoho Contract Management: Streamline Your Business Agreements
Having journeyed through the intricacies of CRM and marketing automation, you are now equipped with the strategic insights and practical knowledge to revolutionize your customer engagement and optimize your operational efficiency. Embrace these powerful technologies not merely as tools, but as vital extensions of your business strategy, enabling you to build deeper relationships, drive measurable growth, and secure your competitive edge in an ever-evolving market. The future of customer-centric business starts now.

Recommended Video
Frequently Asked Questions
What is marketing automation?
Marketing automation refers to software that automates repetitive marketing tasks such as email marketing, social media posting, and ad campaigns.
Why should I integrate CRM and marketing automation?
Integration creates a unified view of the customer, allowing for highly personalized campaigns, improved lead nurturing, and a seamless handoff between marketing and sales.
What are the main benefits of this integration?
Key benefits include increased efficiency, better lead quality, higher conversion rates, improved customer retention, and more accurate marketing ROI tracking.



