Google Tag Manager for SEO: Tracking & Optimization
In the dynamic world of digital marketing, accurate data collection and efficient tag management are paramount for informed decision-making. For SEO professionals, this often translates into the need for robust tracking capabilities without overburdening development teams or slowing down website performance. This is where Google Tag Manager (GTM) emerges as an indispensable tool. Far more than just a container for tracking codes, GTM empowers marketers and SEO specialists to deploy and manage website tags – from analytics to marketing pixels – with unprecedented agility and precision. Understanding how to leverage Google Tag Manager for SEO can unlock deeper insights into user behavior, campaign performance, and ultimately, drive more effective optimization strategies.
💡 Key Takeaways
- GTM simplifies complex tracking setup without direct coding.
- It allows for efficient implementation of SEO-critical elements like structured data (schema).
- Accurate data collection through GTM improves SEO strategy and decision-making.
- Centralized tag management boosts site performance and reduces deployment errors.
“Google Tag Manager isn’t just about analytics; it’s the foundational layer for a robust SEO data strategy, allowing agile implementation of tracking and optimization elements.”
— Dr. Evelyn Reed, Head of Digital Analytics & SEO Strategy
Recommended Tool
Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a robust tag management system that enables marketers and developers to deploy and manage various tracking code snippets (tags) on websites and mobile applications. Its main purpose is to centralize control over these tags, significantly simplifying their deployment, modification, and removal without requiring direct code changes to the underlying website or app.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of GTM, exploring its benefits for search engine optimization, providing practical implementation steps, and demonstrating how it seamlessly integrates with other critical marketing platforms like Google Ads and social media pixels. Whether you’re aiming to improve your website’s organic visibility or fine-tune your paid campaigns, mastering GTM is a non-negotiable skill.
In This Article
- → Google Tag Manager for SEO: Tracking & Optimization
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- — Recommended Tool
- → Why Google Tag Manager is a Game-Changer for SEO
- — Agility and Independence for Marketers
- — Enhanced Data Accuracy and Control
- — Improved Site Performance
- → Setting Up Google Tag Manager for Foundational SEO Tracking
- — 1. Create a GTM Account and Container
- — 2. Install the GTM Code on Your Website
- — 3. Add Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Configuration Tag
- — 4. Verify Your Installation
- → Advanced SEO Tracking & Optimization with Google Tag Manager
- — Tracking User Engagement & Micro-Conversions
- — Custom Events for Deeper Insights
- → Integrating Google Ads and Other Marketing Pixels via Google Tag Manager
- — Seamless Integration with Google Ads Tag Manager
- — Adding Facebook Pixel to Google Tag Manager
- — Other Marketing & Ad Tags
- → Platform-Specific Implementations: Google Tag Manager WordPress Tutorial & Shopify Tag Manager
- — Google Tag Manager WordPress Tutorial: Streamlined Integration
- — Shopify Tag Manager: Enhancing E-commerce Tracking
- → Best Practices, Troubleshooting, and the Future of GTM in SEO
- — Best Practices for GTM Implementation
- — Common Troubleshooting Tips
- — The Future of GTM in SEO
- → Conclusion
Why Google Tag Manager is a Game-Changer for SEO
The core philosophy of SEO is continuous improvement based on data. Google Tag Manager revolutionizes how this data is collected, offering significant advantages over traditional hard-coding of tags directly into website code.
Agility and Independence for Marketers
Historically, every tracking snippet – be it for Google Analytics, Google Ads conversion tracking, or a custom event – required a developer to manually add it to the website’s source code. This process was often slow, prone to errors, and created a bottleneck. GTM eliminates this dependency. Marketers can now deploy, update, or remove tags themselves through a user-friendly interface, significantly speeding up the implementation of new tracking initiatives. This agility is crucial for SEO, allowing rapid testing of new metrics or quick adjustments to tracking based on evolving strategies.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Control
GTM centralizes all your tags in one place, reducing the likelihood of conflicting scripts or duplicate tags that can skew data. With features like version control, preview mode, and debugging tools, you can thoroughly test new tags before pushing them live, ensuring data integrity. This level of control is vital for SEO professionals who rely on accurate data to measure the impact of their optimization efforts, from keyword performance to content engagement.
Improved Site Performance
While often overlooked, how tags are implemented can affect website loading speed, which is a crucial SEO ranking factor. GTM loads tags asynchronously, meaning they don’t block the rendering of other elements on your page. This can contribute to a faster overall load time compared to multiple hard-coded scripts loading synchronously. A faster website enhances user experience, reduces bounce rates, and sends positive signals to search engines.
For a deeper dive into overall SEO strategy, consider exploring The Ultimate Guide to SEO (Search Engine Optimization), which provides foundational knowledge for leveraging tools like GTM effectively.
Setting Up Google Tag Manager for Foundational SEO Tracking
Implementing Google Tag Manager is a straightforward process, but precision is key to ensure all data is captured correctly. Here’s how to get started and set up essential tracking for your SEO efforts.
1. Create a GTM Account and Container
- Go to tagmanager.google.com and sign in with your Google account.
- Click “Create Account” and provide an account name (e.g., your company name) and country.
- Create a “Container” for your website, specifying the target platform (Web, iOS, Android, AMP, Server). For most SEO purposes, “Web” is correct.
- Accept the Terms of Service.
2. Install the GTM Code on Your Website
After creating your container, GTM will provide you with two snippets of code:
- The first snippet should be placed as high as possible in the
<head>section of every page on your website. - The second snippet should be placed immediately after the opening
<body>tag of every page.
It’s critical that these codes are correctly placed on all pages to ensure GTM fires consistently across your site. If you’re using a CMS like WordPress or Shopify, there are easier ways to implement this, which we’ll cover later.
3. Add Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Configuration Tag
Once GTM is installed, the next step is to integrate your analytics platform, most commonly Google Analytics 4 (GA4).
- In your GTM workspace, click “New Tag.”
- Name your tag (e.g., “GA4 – Configuration”).
- Choose “Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration” as the Tag Type.
- Enter your GA4 Measurement ID (e.g., G-XXXXXXXXXX).
- For the Triggering section, select “Initialization – All Pages” to ensure the GA4 base code fires on every page load.
- Save and Publish your container.
This foundational setup is critical. Without it, you won’t be able to collect basic pageview data, which is the cornerstone of any SEO analysis.
4. Verify Your Installation
Before celebrating, always verify your GTM and GA4 setup:
- GTM Preview Mode: In GTM, click “Preview.” Enter your website URL and click “Connect.” This will open your site in a new tab with the GTM debugger active, showing you which tags are firing and when.
- Google Analytics DebugView: In your GA4 property, navigate to “Admin” > “DebugView.” As you browse your site with GTM Preview active, you should see events streaming into DebugView, confirming your GA4 setup is correct.
- Browser Extensions: Tools like the “Tag Assistant Companion” browser extension can also help verify GTM and GA4 tags.
According to Search Engine Journal, using Google Tag Manager can significantly improve your SEO efforts by providing granular control over tracking and enabling more precise data collection. (Source: Search Engine Journal)
Advanced SEO Tracking & Optimization with Google Tag Manager
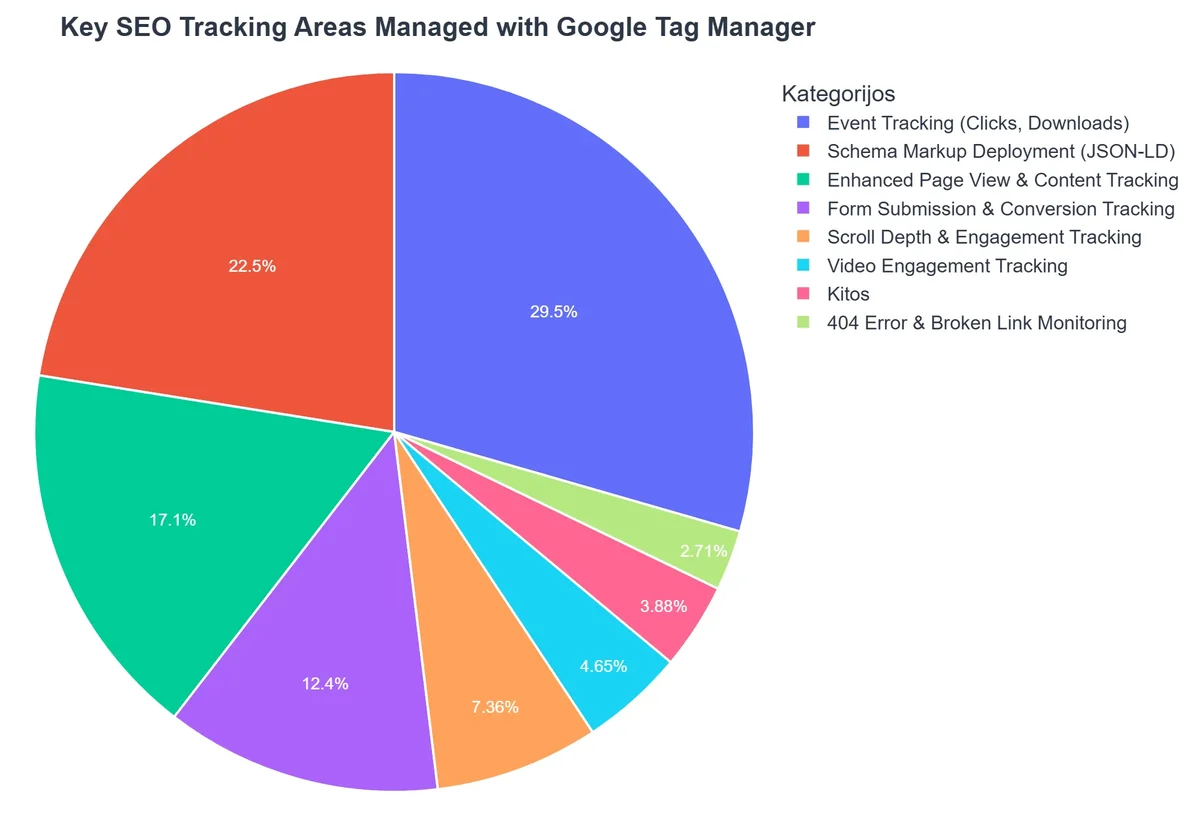
Beyond basic page views, GTM excels at tracking granular user interactions that provide invaluable insights for SEO. These insights help you understand user engagement, content effectiveness, and conversion pathways.
Tracking User Engagement & Micro-Conversions
Identifying what users do on your site beyond just landing on a page is crucial for SEO. GTM allows you to track:
- Scroll Depth: Set up triggers to fire when users scroll 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100% of a page. This helps identify engaging content that keeps users scrolling.
- Element Visibility: Track when specific elements (e.g., images, videos, calls-to-action) come into the user’s viewport. This is excellent for understanding if crucial content is being seen.
- Video Engagement: For websites with embedded videos, GTM can track plays, pauses, complete views, and custom progress points. This is vital for YouTube SEO within WordPress or any other video content strategy.
- Form Submissions: Track successful form submissions, even without a dedicated thank-you page. This helps measure lead generation or contact inquiries directly.
- File Downloads: Monitor when users download PDFs, documents, or other assets, indicating interest in deeper content.
These micro-conversions, while not direct purchases, indicate strong user interest and engagement, which can indirectly influence SEO through improved user signals.
Custom Events for Deeper Insights
The power of GTM lies in its ability to create custom events based on almost any user interaction. For example:
- Click Tracking: Track clicks on specific buttons (e.g., “Add to Cart,” “Download Whitepaper,” internal links to other products). This is invaluable for understanding user journeys and optimizing your site’s navigation.
- Error Tracking: Monitor 404 page views or JavaScript errors. While not directly SEO, consistent errors signal a poor user experience that search engines might penalize.
- Internal Search Tracking: Capture terms users search for within your site. This data is a goldmine for keyword research, revealing unmet content needs and potential new content topics. Combine this with insights from Google Keyword Planner for a comprehensive keyword strategy.
By defining custom events and pushing them to GA4, you gain a granular understanding of user behavior, which in turn informs your content strategy, site structure, and keyword optimization efforts. Effective Keyword Optimization for SEO Success heavily relies on understanding user intent, and custom event tracking can provide direct evidence of that intent on your site.
Integrating Google Ads and Other Marketing Pixels via Google Tag Manager
While GTM is a cornerstone for SEO tracking, its utility extends far beyond, serving as a universal hub for all your marketing pixels. This integration is crucial for measuring the effectiveness of your paid campaigns and understanding the synergy between organic and paid channels.
Seamless Integration with Google Ads Tag Manager
Managing your Google Ads conversion tracking and remarketing tags directly through GTM offers significant advantages. Instead of hard-coding separate snippets for each conversion action (e.g., purchase, lead form, phone call clicks), you can define these as tags in GTM, triggered by specific user behaviors.
To add Google Ads conversion tracking:
- In Google Ads, create a new conversion action and get your Conversion ID and Conversion Label.
- In GTM, create a “New Tag.”
- Choose “Google Ads Conversion Tracking” as the Tag Type.
- Enter your Conversion ID and Conversion Label.
- Set the Trigger based on the desired conversion event (e.g., a “Thank You” page view, a custom event for form submission).
- Publish your container.
This process makes it much easier to deploy and manage multiple conversion points for various campaigns, ensuring accurate measurement of your return on ad spend. The efficiency of using Google Ads Tag Manager cannot be overstated, especially for businesses running complex campaigns.
Adding Facebook Pixel to Google Tag Manager
Beyond Google’s ecosystem, GTM is the go-to solution for managing third-party marketing pixels, most notably the Facebook Pixel. This is essential for running effective Facebook/Instagram ad campaigns, building custom audiences, and tracking conversions.
Steps to add Facebook Pixel to Google Tag Manager:
Google Tag Manager for SEO: Tracking & Optimization Review
Pros
- ✔Simplifies tracking code deployment, reducing developer dependency.
- ✔Enables advanced custom tracking for deeper SEO insights (e.g., user engagement).
- ✔Offers version control and debugging tools for safer tag management.
- ✔Potentially improves site performance by asynchronously loading scripts.
Cons
- ✖Requires a significant learning curve for effective use.
- ✖Risk of data inaccuracies or broken tracking if misconfigured.
- ✖Can introduce performance overhead if too many tags are poorly managed.
- ✖Demands ongoing maintenance and careful planning.
- From your Facebook Business Manager, navigate to Events Manager and retrieve your Facebook Pixel ID.
- In GTM, create a “New Tag.”
- Choose “Custom HTML” as the Tag Type.
- Paste the entire base Facebook Pixel code (the one provided by Facebook for initial installation) into the HTML field.
- Set the Trigger to “All Pages” (Page View) to ensure the base pixel fires on every page load.
- To track standard events (e.g., ViewContent, AddToCart, Purchase) or custom events, you’ll need to create separate “Custom HTML” tags or use a custom template, firing them based on specific GTM triggers that correspond to those user actions.
- Publish your container.
This centralized approach means you only need to manage the pixel code within GTM, simplifying updates and troubleshooting. Learning how to add Facebook Pixel to Google Tag Manager is a fundamental step for any business leveraging social media advertising.
Other Marketing & Ad Tags
GTM supports a vast array of other marketing platforms, allowing you to centralize tags for:
- LinkedIn Insight Tag
- Pinterest Tag
- TikTok Pixel
- Hotjar/Crazy Egg (heatmaps & session recordings)
- Intercom/Drift (live chat widgets)
- A/B testing tools (e.g., Google Optimize, Optimizely)
This consolidation prevents code bloat, reduces errors, and gives marketers the autonomy to manage their tracking tools without constant developer intervention. This contributes to better Landing Page Optimization, as you can quickly deploy new tracking for A/B tests or conversion funnels.
Platform-Specific Implementations: Google Tag Manager WordPress Tutorial & Shopify Tag Manager
While the core principles of GTM remain the same, integrating it into popular content management systems (CMS) and e-commerce platforms often involves specific best practices to ensure seamless functionality.
Google Tag Manager WordPress Tutorial: Streamlined Integration
For WordPress users, manually editing header.php or functions.php files for GTM installation is possible but not recommended due to potential errors and updates overwriting changes. The most reliable and user-friendly method is to use a dedicated plugin.
Recommended WordPress GTM Integration Plugin:
The “Site Kit by Google” plugin is the official and most comprehensive way to integrate Google services, including Google Tag Manager, Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and Google Ads, directly into your WordPress dashboard.
- Install and Activate Site Kit: From your WordPress dashboard, go to Plugins > Add New, search for “Site Kit by Google,” install, and activate it.
- Connect Services: Follow the setup wizard to connect your Google account. You’ll be prompted to connect Search Console, Analytics, and then Tag Manager.
- Select GTM Container: During the setup, Site Kit will ask you to select your existing GTM container from a dropdown list. If you haven’t created one yet, do so on the GTM website first.
- Verify: Once connected, Site Kit will automatically place the GTM code snippets in the correct locations across your WordPress site. Verify the installation using GTM’s Preview mode as described earlier.
Using a plugin like Site Kit simplifies the initial setup and ensures the GTM code is correctly placed on all pages, including posts, pages, and custom post types, which is crucial for comprehensive SEO tracking on WordPress.
Shopify Tag Manager: Enhancing E-commerce Tracking
Shopify, being a hosted e-commerce platform, has specific areas where you can add custom scripts. While less flexible than WordPress for direct theme file editing, Shopify Tag Manager integration is robust.
Steps to add Google Tag Manager to Shopify:
- Copy GTM Container Snippets: In your GTM workspace, find your container ID (e.g., GTM-XXXXXXX). Note the two snippets of code.
- Theme.liquid (Head Snippet):
- From your Shopify Admin, go to Online Store > Themes.
- Click “Actions” > “Edit code” for your current theme.
- Locate
theme.liquidunder “Layout.” - Paste the first GTM snippet (the one for
<head>) immediately after the opening<head>tag. - Save the file.
- Checkout Settings (Body Snippet & Additional Scripts):
- From your Shopify Admin, go to Settings > Checkout.
- Scroll down to the “Order status page” section.
- In the “Additional scripts” box, paste the second GTM snippet (the one for
<body>). This ensures GTM loads on the thank-you page after a purchase. - Additionally, for e-commerce tracking, you’ll need to set up data layer variables within Shopify’s theme files or through a custom app to pass purchase data (product IDs, prices, quantities) to the GTM data layer. This is more advanced and often requires developer assistance or a dedicated Shopify GTM app.
- Verify: Use GTM’s Preview mode and GA4’s DebugView to confirm that tags are firing correctly, especially on product pages, cart, and the thank-you page.
Proper GTM implementation on Shopify is vital for tracking crucial e-commerce events like “Add to Cart,” “Checkout Initiated,” and “Purchase,” which provide direct insights into your conversion funnel and contribute significantly to overall SEO performance by highlighting successful product pages and user journeys.
Best Practices, Troubleshooting, and the Future of GTM in SEO
To maximize the benefits of Google Tag Manager for your SEO and marketing efforts, adhering to best practices and understanding common pitfalls is essential. Furthermore, staying abreast of GTM’s evolution will ensure your tracking strategies remain effective.
Best Practices for GTM Implementation
- Use Clear Naming Conventions: Consistent naming for tags, triggers, and variables makes your GTM container manageable and understandable for anyone working on it.
- Leverage the Data Layer: The data layer is the bridge between your website and GTM. Push relevant data (e.g., user ID, product details, content category) into the data layer to create highly specific triggers and variables for advanced tracking.
- Test Thoroughly with Preview Mode: Never publish a new tag or change without testing it in GTM’s Preview mode. This prevents deploying broken tracking and ensures data integrity.
- Utilize Version Control: GTM automatically saves versions of your container. Use the “Add Version” and “Publish” feature with detailed notes for each change. This allows for easy rollbacks if issues arise.
- Keep Your Container Clean: Regularly review and remove old, unused tags, triggers, and variables. A bloated container can be difficult to manage and potentially impact performance.
- Document Your Setup: Maintain external documentation of your GTM setup, including complex custom events, data layer implementations, and variable definitions.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
- GTM Code Not Firing: Double-check that both GTM code snippets are correctly placed on all pages of your site (one in
<head>, one after<body>). Use browser developer tools to inspect the page source. - Tags Not Firing: Use GTM’s Preview mode. If a tag isn’t firing, check its trigger conditions. Are they specific enough? Are they too broad? Is the event it’s listening for actually happening?
- Incorrect Data in Analytics: If data appears in GA4 but is wrong (e.g., duplicate events, missing values), check your variables in GTM. Ensure they are correctly extracting information from the data layer or DOM elements.
- Conflicting Scripts: While GTM helps reduce this, sometimes external scripts or plugins can interfere. Use the browser console to check for JavaScript errors.
The Future of GTM in SEO
As privacy regulations (like GDPR and CCPA) become stricter and third-party cookies phase out, GTM is adapting. Server-side tagging, a feature within GTM, is gaining prominence. This allows data collection to occur on your server rather than directly from the user’s browser, enhancing control over data, potentially improving site performance, and offering more robust first-party data collection methods. While server-side GTM is more complex to set up, it represents a significant shift that SEO professionals will increasingly need to understand to maintain accurate and compliant tracking.
Recommended Video
Conclusion
In the competitive landscape of digital marketing, the ability to accurately track, analyze, and optimize is what separates successful SEO strategies from those that falter. Google Tag Manager for SEO is not just a convenience; it’s a critical infrastructure component that empowers marketers with unparalleled control over their website’s data collection. From deploying foundational Google Analytics tags to intricate custom event tracking and seamless integration with Google Ads and Facebook Pixel, GTM streamlines operations, enhances data quality, and accelerates the pace of optimization.
By mastering GTM, SEO professionals can gain deeper insights into user behavior, measure the true impact of their content, and react swiftly to new opportunities or challenges. As the digital ecosystem continues to evolve, embracing powerful tools like Google Tag Manager will be paramount for maintaining a competitive edge and driving sustainable organic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
GTM is a tag management system that allows you to quickly and easily update tracking codes and related code snippets, known as “tags,” on your website or mobile app without modifying the site’s code directly.
How does GTM benefit SEO?
GTM helps SEO by enabling precise tracking of user behavior, simplifying the deployment of structured data (schema markup), and facilitating the implementation of custom analytics events crucial for optimization insights.
Can I use GTM for A/B testing?
Yes, GTM can be used to deploy and manage scripts for A/B testing tools, allowing you to easily test different website elements and content variations for SEO performance and user experience.
Is coding knowledge required to use GTM?
While basic HTML/CSS knowledge is helpful, GTM significantly reduces the need for direct code manipulation on your website, allowing marketers to manage tags and tracking without relying heavily on developers.