Ecommerce SEO & Email Marketing: Effective Strategies
In the competitive world of online retail, standing out and converting visitors into loyal customers requires more than just a great product. It demands a holistic approach to digital marketing. While Search Engine Optimization (SEO) excels at driving qualified organic traffic to your store, and email marketing nurtures those leads and fosters repeat business, their true power emerges when they are seamlessly integrated. This guide will reveal how combining a robust seo strategy for ecommerce website with intelligent email marketing can unlock unprecedented growth for your online store.
Shopify
Shopify isn’t just an e-commerce platform; it’s your all-in-one command center for online sales. From stunning storefronts that convert, to secure payment processing and streamlined inventory management, Shopify empowers entrepreneurs of all sizes to launch, run, and scale their businesses with remarkable ease. Stop wrestling with complex tech and start focusing on growth – Shopify provides the robust, intuitive foundation you need to turn visitors into loyal customers and ideas into thriving empires.
💡 Key Takeaways
- Integrating SEO and email marketing amplifies ecommerce growth by addressing distinct parts of the customer journey.
- SEO drives organic discovery and awareness, while email nurtures direct relationships and encourages repeat purchases.
- Data-driven personalization is crucial for optimizing both SEO content for user intent and email campaigns for higher engagement.
- Consistent brand messaging and user experience across all digital channels significantly boost conversion rates and customer loyalty.
“The true power of ecommerce growth lies in harmonizing SEO with email marketing. SEO attracts, and email converts and retains, creating an unbeatable customer lifecycle that builds sustainable revenue.”
— Victoria Nelson, Ecommerce SEO Specialist
Think of it this way: SEO brings the potential customers to your digital storefront, and email marketing transforms them from window shoppers into paying customers, and ultimately, brand advocates. This powerful synergy not only maximizes your visibility but also dramatically improves your customer lifetime value (CLTV).
In This Article
- → Ecommerce SEO & Email Marketing: Effective Strategies
- — 💡 Key Takeaways
- → The Synergistic Power of SEO and Email Marketing
- — 🤝 Bridging the Gap Between Discovery and Conversion
- — 📈 Amplifying Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
- → Foundational SEO Strategies for E-commerce Success
- — 🔍 Keyword Research for Product Pages
- — 🏗️ Technical SEO Essentials for Online Stores
- — 📝 Optimizing Product Descriptions and Category Pages
- → Crafting an Effective Email Marketing Strategy for E-commerce
- — 📧 Building Your Email List Organically
- — 🎯 Segmenting Your Audience for Personalization
- — 🛒 Essential E-commerce Email Flows
- → Integrating SEO & Email for Maximum Impact
- — 🔄 Leveraging SEO-Driven Content in Emails
- — ⭐ Collecting Reviews for SEO & Social Proof
- — 🔗 Driving Traffic to Optimized Pages via Email
- → Measuring Success & Iterating Your Strategy
- — 📊 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- — 🧪 A/B Testing and Continuous Optimization
- → Conclusion
The Synergistic Power of SEO and Email Marketing
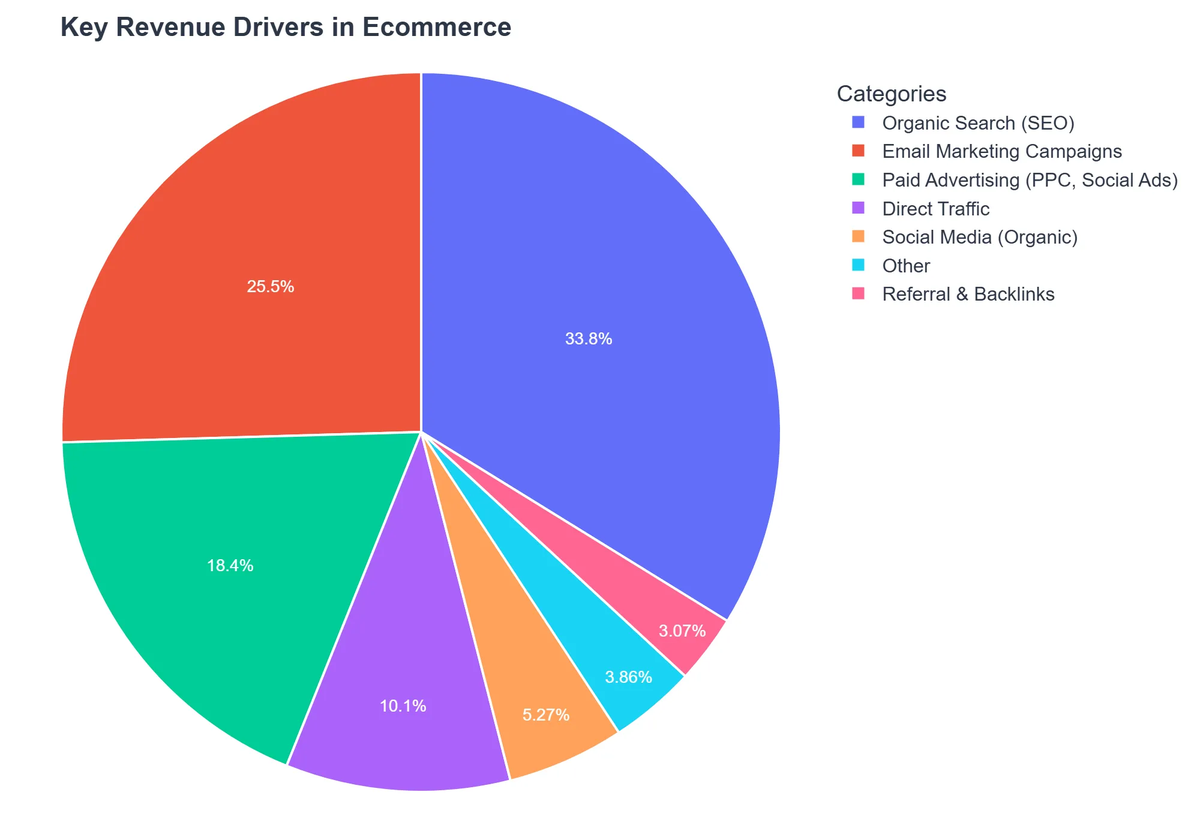
Many e-commerce businesses treat SEO and email marketing as separate disciplines. However, by understanding how they complement each other, you can build a more resilient and effective marketing ecosystem. SEO focuses on long-term organic visibility and attracting new prospects, while email marketing nurtures relationships and drives conversions directly.
🤝 Bridging the Gap Between Discovery and Conversion
SEO’s primary role is to ensure your products and content are discoverable when potential customers search for them. This brings high-intent traffic to your site. Email marketing then takes over, allowing you to:
- ✅ Capture leads who might not be ready to buy immediately.
- ✅ Provide personalized content that addresses their specific needs or interests.
- ✅ Remind them of abandoned carts.
- ✅ Announce new products or sales, driving repeat visits and purchases.
📈 Amplifying Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
While SEO helps acquire new customers, email marketing is a powerhouse for retention and increasing CLTV. By segmenting your audience and sending targeted campaigns, you can encourage repeat purchases, solicit reviews (which benefit SEO), and build a community around your brand.
Foundational SEO Strategies for E-commerce Success
Before you can integrate email marketing effectively, you need a solid e-commerce SEO foundation. This ensures you’re attracting the right audience in the first place. Platforms like Shopify, for instance, provide many built-in SEO features, but true optimization requires a strategic approach.
For a comprehensive understanding, consult our Ecommerce SEO: The Definitive Guide for Online Stores.
🔍 Keyword Research for Product Pages
Effective e-commerce SEO begins with in-depth keyword research. You need to understand exactly what your potential customers are searching for. This goes beyond just product names:
- ➡️ Short-tail keywords: Broad terms (e.g., “running shoes”).
- ➡️ Long-tail keywords: Specific phrases with higher purchase intent (e.g., “men’s black waterproof running shoes size 10”).
- ➡️ Competitor analysis: See what keywords your competitors rank for.
- ➡️ User intent: Are they looking to buy, or just research?
Integrate these keywords naturally into product titles, descriptions, image alt text, and URLs.
🏗️ Technical SEO Essentials for Online Stores
A technically sound website is crucial for search engine crawling and indexing. Key aspects include:
- 💡 Site Speed: Fast loading times improve user experience and search rankings.
- 💡 Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your site is responsive and performs well on all devices.
- 💡 Structured Data (Schema Markup): Use schema (e.g., Product, Review, Offer) to help search engines understand your content and display rich snippets.
- 💡 XML Sitemaps & Robots.txt: Guide search engine bots through your site.
- 💡 Secure (HTTPS) Protocol: Essential for trust and SEO.
For more accessible SEO tactics, check out Simplifying E-commerce SEO: Easy Strategies for Online Stores.
📝 Optimizing Product Descriptions and Category Pages
Beyond keywords, your content must be compelling and informative. Each product and category page is an opportunity to rank:
- ✅ Unique, detailed descriptions: Avoid manufacturer boilerplate text.
- ✅ High-quality images/videos: With optimized alt text.
- ✅ Clear calls-to-action (CTAs): Encourage conversion.
- ✅ Internal linking: Link related products and categories to improve site structure and user flow.
Crafting an Effective Email Marketing Strategy for E-commerce
Once traffic arrives, email marketing takes over. Email boasts an impressive ROI and is a direct line to your customers. As OuterBox Design explains, email marketing involves “sending commercial messages to a group of people using email,” but for e-commerce, it’s about building relationships and driving sales. Learn more about the basics of email marketing here.
📧 Building Your Email List Organically
Your SEO efforts can directly feed your email list:
- 💡 Pop-ups & Exit-intent forms: Offer a discount or exclusive content in exchange for an email.
- 💡 Content Upgrades: Create valuable, SEO-optimized blog posts, and offer a downloadable guide (e.g., “The Ultimate Guide to [Product Category]”) that requires an email sign-up.
- 💡 Footer & Sidebar Forms: Provide persistent options for sign-ups.
- 💡 Post-purchase opt-in: Offer an option to subscribe during checkout.
🎯 Segmenting Your Audience for Personalization
Generic emails yield poor results. Segmentation allows for targeted, relevant communication:
- ✅ Purchase history: Customers who bought Product X might be interested in accessories.
- ✅ Browse behavior: Visitors who viewed specific categories but didn’t buy.
- ✅ Geographic location: For local promotions or shipping updates.
- ✅ Engagement level: Send different content to highly engaged vs. dormant subscribers.
🛒 Essential E-commerce Email Flows
Automated email sequences are the backbone of e-commerce email marketing:
- ➡️ Welcome Series: Greet new subscribers, introduce your brand, and offer a first-purchase discount.
- ➡️ Abandoned Cart Emails: Remind customers about items left in their cart. These have incredibly high conversion rates.
- ➡️ Post-Purchase & Review Request Emails: Thank customers, provide shipping info, and later, ask for product reviews (crucial for SEO!).
- ➡️ Win-Back Campaigns: Re-engage inactive customers with special offers.
- ➡️ Promotional & Sale Announcements: Keep customers informed about deals and new arrivals.
Integrating SEO & Email for Maximum Impact
This is where the magic happens. By intentionally connecting your SEO and email efforts, you create a powerful flywheel effect.
🔄 Leveraging SEO-Driven Content in Emails
Your blog and content marketing efforts are great for SEO. Don’t let them sit idle. Share them with your email list:
Ecommerce SEO & Email Marketing: Pros and Cons
Pros
- ✔Drives sustainable organic traffic and improves brand visibility.
- ✔High ROI potential through targeted campaigns and direct customer engagement.
- ✔Fosters customer loyalty, retention, and repeat purchases.
- ✔Creates a synergistic effect, enhancing overall conversion rates.
Cons
- ✖SEO requires significant time and ongoing effort for results.
- ✖Constant adaptation needed due to algorithm changes and market competition.
- ✖Challenges with email deliverability, open rates, and avoiding spam filters.
- ✖Can be resource-intensive in terms of content creation, tools, and expertise.
- ✅ Promote new blog posts in newsletters, driving traffic back to your optimized content.
- ✅ Use educational content (e.g., “How to Choose the Right [Product]”) in email sequences to guide purchase decisions.
- ✅ Link directly to SEO-optimized product category pages within your emails.
⭐ Collecting Reviews for SEO & Social Proof
Customer reviews are gold for both SEO and conversion rates. Email marketing is your most effective tool for gathering them:
- 💡 Automated Review Request Emails: Send these after a purchase, asking customers to leave a review directly on your product page.
- 💡 Incentivize Reviews: Offer a small discount on future purchases for leaving a review.
- 💡 Display Reviews Prominently: Ensure reviews are visible on product pages, which search engines love.
🔗 Driving Traffic to Optimized Pages via Email
Use your email campaigns to direct subscribers to specific, highly optimized pages on your site:
- ➡️ New Product Launches: Drive traffic to new product pages that you’ve optimized for relevant keywords.
- ➡️ Seasonal Campaigns: Point customers to landing pages created for specific holidays or sales events.
- ➡️ Back-in-Stock Alerts: Notify subscribers when a popular, previously out-of-stock item is available again, driving immediate, high-intent traffic to its product page.
Tools like Omnisend for E-commerce: A Guide to Growth can help streamline these integrated efforts.
Measuring Success & Iterating Your Strategy
To ensure your combined SEO and email marketing efforts are paying off, consistent monitoring and analysis are critical. As TechTarget highlights, effective e-commerce marketing involves “a clear understanding of your goals, target audience, and how to reach them.”
Discover more e-commerce marketing strategies from TechTarget.
📊 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Track metrics for both channels and how they influence each other:
- ✅ SEO KPIs: Organic traffic, keyword rankings, conversion rate from organic traffic, bounce rate.
- ✅ Email Marketing KPIs: Open rate, click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate from email campaigns, unsubscribe rate, revenue per email sent.
- ✅ Integrated KPIs: Revenue generated from email marketing that originated from organic search, impact of review requests on organic visibility.
🧪 A/B Testing and Continuous Optimization
Digital marketing is an iterative process. Continually test and refine your strategies:
- 💡 SEO A/B Tests: Test different meta descriptions, titles, or page layouts for their impact on CTR and rankings.
- 💡 Email A/B Tests: Experiment with subject lines, email copy, CTA buttons, and send times.
- 💡 Customer Journey Mapping: Analyze how customers move from organic search to email engagement and then to conversion.
Recommended Video
The convergence of e-commerce SEO and email marketing is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how successful online businesses operate. By strategically aligning your efforts to attract visitors through search and then nurture them through personalized email communication, you create a powerful, sustainable engine for growth. Embrace this integrated approach, continuously measure your results, and adapt your strategies to build a highly visible, engaging, and profitable online store.
How does SEO enhance email marketing efforts?
SEO drives organic traffic to your site, providing a larger, qualified pool of potential subscribers for your email lists. High-ranking content can also be repurposed for email campaigns.
Can email marketing indirectly improve my SEO?
Yes, indirectly. Email campaigns can drive engaged traffic to key landing pages, increase time on site, reduce bounce rates, and encourage social shares, all of which send positive signals to search engines.
What key metrics should I track for an integrated strategy?
Focus on metrics like organic traffic, email subscriber growth, conversion rates (from both channels), customer lifetime value (CLTV), average order value (AOV), and customer retention rates.
Should I use the same content for SEO and email marketing?
While content can be repurposed, it’s best to tailor it for each channel. Use SEO to create comprehensive, authoritative guides, and email to deliver concise updates, promotions, or personalized recommendations based on user behavior.
Shopify
Ready to take the next step? See how Shopify can help you achieve your goals.